Regulation of type I interferon responses
- PMID: 24362405
- PMCID: PMC4084561
- DOI: 10.1038/nri3581
Regulation of type I interferon responses
Abstract
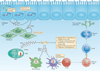
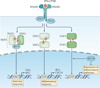
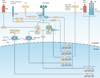
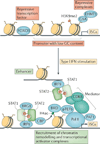
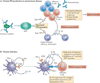
Type I interferons (IFNs) activate intracellular antimicrobial programmes and influence the development of innate and adaptive immune responses. Canonical type I IFN signalling activates the Janus kinase (JAK)-signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) pathway, leading to transcription of IFN-stimulated genes (ISGs). Host, pathogen and environmental factors regulate the responses of cells to this signalling pathway and thus calibrate host defences while limiting tissue damage and preventing autoimmunity. Here, we summarize the signalling and epigenetic mechanisms that regulate type I IFN-induced STAT activation and ISG transcription and translation. These regulatory mechanisms determine the biological outcomes of type I IFN responses and whether pathogens are cleared effectively or chronic infection or autoimmune disease ensues.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

