Structure and antioxidant activity of polyphenols derived from propolis
- PMID: 24362627
- PMCID: PMC6271064
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules19010078
Structure and antioxidant activity of polyphenols derived from propolis
Abstract
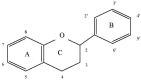
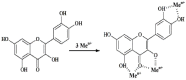
Propolis is a potential source of natural antioxidants such as phenolic acids and flavonoids. Its wide biological effects have been known and used since antiquity. In the modern world natural substances are sought which would be able to counteract the effects of antioxidative stress, which underlies many diseases, such as cancer, diabetes and atherosclerosis. This paper aims to present the antioxidative activity of phenolic acids and flavonoids present in Polish propolis and the relationship between their chemical structure and antioxidative activity influencing its medicinal properties. Data concerning the biological activity of propolis are summarized here, including its antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, anticarcinogenic, antiatherogenic, estrogenic effects, as well as AIDS- counteracting and reparative-regenerative function.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Kędzia B. Chemical composition of polish propolis. Part I. The initial period of investigations. Post. Fitoter. 2009;1:39–44.
-
- Kędzia B. Chemical composition of polish propolis. Part II. New Studies. Post. Fitoter. 2009;2:122–128.
-
- Olczyk P., Komosińska-Vassev K., Olczyk K. Propolis-chemical composition, properties and application. Farm. Pol. 2007;63:1102–1107.
-
- Kędzia B., Hołderna-Kędzia E. Chemical composition of propolis in nowadays researches. Herba Pol. 1991;38:95–107.
-
- Khalil M.L. Biological activity of bee propolis in health and disease. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2006;7:22–31. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical