Structure and function of respiratory syncytial virus surface glycoproteins
- PMID: 24362685
- PMCID: PMC4211642
- DOI: 10.1007/978-3-642-38919-1_4
Structure and function of respiratory syncytial virus surface glycoproteins
Abstract
The two major glycoproteins on the surface of the respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) virion, the attachment glycoprotein (G) and the fusion glycoprotein (F), control the initial phases of infection. G targets the ciliated cells of the airways, and F causes the virion membrane to fuse with the target cell membrane. The F protein is the major target for antiviral drug development, and both G and F glycoproteins are the antigens targeted by neutralizing antibodies induced by infection. In this chapter, we review the structure and function of the RSV surface glycoproteins, including recent X-ray crystallographic data of the F glycoprotein in its pre- and postfusion conformations, and discuss how this information informs antigen selection and vaccine development.
Figures
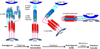
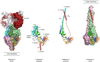

References
-
- Arumugham RG, Seid RC, Doyle S, Hildreth SW, Paradiso PR. Fatty acid acylation of the fusion glycoprotein of human respiratory syncytial virus. J Biol Chem. 1989;264(18):10339–10342. - PubMed
-
- Barr FE, Pedigo H, Johnson TR, Shepherd VL. Surfactant protein-A enhances uptake of respiratory syncytial virus by monocytes and U937 macrophages. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2000;23(5):586–592. - PubMed
-
- Begona Ruiz-Arguello M, Gonzalez-Reyes L, Calder LJ, Palomo C, Martin D, Saiz MJ, Garcia-Barreno B, Skehel JJ, Melero JA. Effect of proteolytic processing at two distinct sites on shape and aggregation of an anchorless fusion protein of human respiratory syncytial virus and fate of the intervening segment. Virology. 2002;298(2):317–326. - PubMed
-
- Behera AK, Matsuse H, Kumar M, Kong X, Lockey RF, Mohapatra SS. Blocking intercellular adhesion molecule-1 on human epithelial cells decreases respiratory syncytial virus infection. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2001;280(1):188–195. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

