Everolimus plus exemestane as first-line therapy in HR⁺, HER2⁻ advanced breast cancer in BOLERO-2
- PMID: 24362951
- PMCID: PMC3907668
- DOI: 10.1007/s10549-013-2814-5
Everolimus plus exemestane as first-line therapy in HR⁺, HER2⁻ advanced breast cancer in BOLERO-2
Abstract
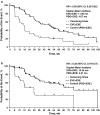
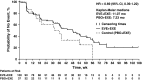
The present exploratory analysis examined the efficacy, safety, and quality-of-life effects of everolimus (EVE) + exemestane (EXE) in the subgroup of patients in BOLERO-2 whose last treatment before study entry was in the (neo)adjuvant setting. In BOLERO-2, patients with hormone-receptor-positive (HR(+)), human epidermal growth factor receptor-2-negative (HER2(-)) advanced breast cancer recurring/progressing after a nonsteroidal aromatase inhibitor (NSAI) were randomly assigned (2:1) to receive EVE (10 mg/day) + EXE (25 mg/day) or placebo (PBO) + EXE. The primary endpoint was progression-free survival (PFS) by local assessment. Overall, 137 patients received first-line EVE + EXE (n = 100) or PBO + EXE (n = 37). Median PFS by local investigator assessment nearly tripled to 11.5 months with EVE + EXE from 4.1 months with PBO + EXE (hazard ratio = 0.39; 95 % CI 0.25-0.62), while maintaining quality of life. This was confirmed by central assessment (15.2 vs 4.2 months; hazard ratio = 0.32; 95 % CI 0.18-0.57). The marked PFS improvement in patients receiving EVE + EXE as first-line therapy for disease recurrence during or after (neo)adjuvant NSAI therapy supports the efficacy of this combination in the first-line setting. Furthermore, the results highlight the potential benefit of early introduction of EVE + EXE in the management of HR(+), HER2(-) advanced breast cancer in postmenopausal patients.
Figures
References
-
- Cardoso F, Costa A, Norton L, Cameron D, Cufer T, Fallowfield L, Francis P, Gligorov J, Kyriakides S, Lin N, Pagani O, Senkus E, Thomssen C, Aapro M, Bergh J, Di Leo A, El Saghir N, Ganz PA, Gelmon K, Goldhirsch A, Harbeck N, Houssami N, Hudis C, Kaufman B, Leadbeater M, Mayer M, Rodger A, Rugo H, Sacchini V, Sledge G, van’t Veer L, Viale G, Krop I, Winer E. 1st International consensus guidelines for advanced breast cancer (ABC 1) Breast. 2012;21(3):242–252. doi: 10.1016/j.breast.2012.03.003. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cardoso F, Harbeck N, Fallowfield L, Kyriakides S, Senkus E (2012) Locally recurrent or metastatic breast cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol 23(Suppl 7):vii11–19. doi:10.1093/annonc/mds232 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

