Licking microstructure reveals rapid attenuation of neophobia
- PMID: 24363269
- PMCID: PMC3921893
- DOI: 10.1093/chemse/bjt069
Licking microstructure reveals rapid attenuation of neophobia
Abstract
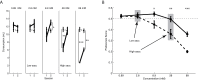
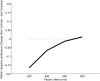
Many animals hesitate when initially consuming a novel food and increase their consumption of that food between the first and second sessions of access-a process termed attenuation of neophobia (AN). AN has received attention as a model of learning and memory; it has been suggested that plasticity resulting from an association of the novel tastant with "safe outcome" results in a change in the neural response to the tastant during the second session, such that consumption increases. Most studies have reported that AN emerges only an hour or more after the end of the first exposure to the tastant, consistent with what is known of learning-related plasticity. But these studies have typically measured consumption, rather than real-time behavior, and thus the possibility exists that a more rapidly developing AN remains to be discovered. Here, we tested this possibility, examining both consumption and individual lick times in a novel variant of a brief-access task (BAT). When quantified in terms of consumption, data from the BAT accorded well with the results of a classic one-bottle task-both revealed neophobia/AN specific to higher concentrations (for instance, 28mM) of saccharin. An analysis of licking microstructure, however, additionally revealed a real-time correlate of neophobia-an explicit tendency, similarly specific for 28-mM saccharin, to cut short the initial bout of licks in a single trial (compared with water). This relative hesitancy (i.e., the shortness of the first lick bout to 28-mM saccharin compared with water) that constitutes neophobia not only disappeared between sessions but also gradually declined in magnitude across session 1. These data demonstrate that the BAT accurately measures AN, and that aspects of AN-and the processes underlying familiarization-begin within minutes of the very first taste.
Keywords: attenuation of neophobia; brief-access task; licking microstructure.
Figures





References
-
- Abel T, Kandel E. 1998. Positive and negative regulatory mechanisms that mediate long-term memory storage. Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 26:360–378 - PubMed
-
- Aguado L, Symonds M, Hall G. 1994. Interval between preexposure and test determines the magnitude of latent inhibition - implications for an interference account. Anim Learn Behav. 22:188–194
-
- Allison J, Castellan J. 1970. Temporal characteristics of nutritive drinking in rats and humans. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 70:116–125
-
- Bahar AS, Dudai Y, Ahissar E. 2004. Neural signature of taste familiarity in the gustatory cortex of the freely behaving rat. J Neurophysiol. 92:3298–3308 - PubMed
-
- Bartoshuk LM. 1979. Bitter taste of saccharin related to the genetic ability to taste the bitter substance 6-n-propylthiouracil. Science. 205:934–935 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

