Sufficient amounts of functional HOP2/MND1 complex promote interhomolog DNA repair but are dispensable for intersister DNA repair during meiosis in Arabidopsis
- PMID: 24363313
- PMCID: PMC3903996
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.113.118521
Sufficient amounts of functional HOP2/MND1 complex promote interhomolog DNA repair but are dispensable for intersister DNA repair during meiosis in Arabidopsis
Abstract
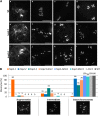
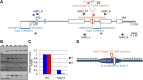
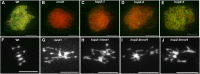
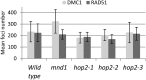
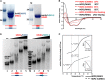
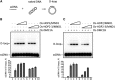
During meiosis, homologous recombination (HR) is essential to repair programmed DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs), and a dedicated protein machinery ensures that the homologous chromosome is favored over the nearby sister chromatid as a repair template. The homologous-pairing protein2/meiotic nuclear division protein1 (HOP2/MND1) protein complex has been identified as a crucial factor of meiotic HR in Arabidopsis thaliana, since loss of either MND1 or HOP2 results in failure of DNA repair. We isolated two mutant alleles of HOP2 (hop2-2 and hop2-3) that retained the capacity to repair meiotic DSBs via the sister chromatid but failed to use the homologous chromosome. We show that in these alleles, the recombinases radiation sensitive51 (RAD51) and disrupted meiotic cDNA1 (DMC1) are loaded, but only the intersister DNA repair pathway is activated. The hop2-2 phenotype is correlated with a decrease in HOP2/MND1 complex abundance. In hop2-3, a truncated HOP2 protein is produced that retains its ability to bind to DMC1 and DNA but forms less stable complexes with MND1 and fails to efficiently stimulate DMC1-driven D-loop formation. Genetic analyses demonstrated that in the absence of DMC1, HOP2/MND1 is dispensable for RAD51-mediated intersister DNA repair, while in the presence of DMC1, a minimal amount of functional HOP2/MND1 is essential to drive intersister DNA repair.
Figures

Comment in
-
Embracing diversity: uncovering the mechanism underlying interhomologous recombination bias during meiosis.Plant Cell. 2013 Dec;25(12):4770. doi: 10.1105/tpc.113.251211. Epub 2013 Dec 20. Plant Cell. 2013. PMID: 24363311 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
The recombinases DMC1 and RAD51 are functionally and spatially separated during meiosis in Arabidopsis.Plant Cell. 2012 May;24(5):2058-70. doi: 10.1105/tpc.112.098459. Epub 2012 May 15. Plant Cell. 2012. PMID: 22589466 Free PMC article.
-
MCM8 is required for a pathway of meiotic double-strand break repair independent of DMC1 in Arabidopsis thaliana.PLoS Genet. 2013;9(1):e1003165. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003165. Epub 2013 Jan 3. PLoS Genet. 2013. PMID: 23300481 Free PMC article.
-
Mnd1/Hop2 facilitates Dmc1-dependent interhomolog crossover formation in meiosis of budding yeast.Mol Cell Biol. 2006 Apr;26(8):2913-23. doi: 10.1128/MCB.26.8.2913-2923.2006. Mol Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16581767 Free PMC article.
-
The Hop2-Mnd1 Complex and Its Regulation of Homologous Recombination.Biomolecules. 2023 Apr 10;13(4):662. doi: 10.3390/biom13040662. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 37189409 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Repair of DNA double-strand breaks in plant meiosis: role of eukaryotic RecA recombinases and their modulators.Plant Reprod. 2023 Mar;36(1):17-41. doi: 10.1007/s00497-022-00443-6. Epub 2022 Jun 1. Plant Reprod. 2023. PMID: 35641832 Review.
Cited by
-
Significance of ligand interactions involving Hop2-Mnd1 and the RAD51 and DMC1 recombinases in homologous DNA repair and XX ovarian dysgenesis.Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Apr 30;43(8):4055-66. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv259. Epub 2015 Mar 27. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015. PMID: 25820426 Free PMC article.
-
Oryza sativa RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase 6 Contributes to Double-Strand Break Formation in Meiosis.Plant Cell. 2020 Oct;32(10):3273-3289. doi: 10.1105/tpc.20.00213. Epub 2020 Jul 30. Plant Cell. 2020. PMID: 32732308 Free PMC article.
-
MS5 Mediates Early Meiotic Progression and Its Natural Variants May Have Applications for Hybrid Production in Brassica napus.Plant Cell. 2016 Jun;28(6):1263-78. doi: 10.1105/tpc.15.01018. Epub 2016 May 18. Plant Cell. 2016. PMID: 27194707 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome Analysis of Floral Buds Deciphered an Irregular Course of Meiosis in Polyploid Brassica rapa.Front Plant Sci. 2017 May 12;8:768. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2017.00768. eCollection 2017. Front Plant Sci. 2017. PMID: 28553302 Free PMC article.
-
FIGL1 attenuates meiotic interhomolog repair and is counteracted by the RAD51 paralog XRCC2 and the chromosome axis protein ASY1 during meiosis.New Phytol. 2024 Dec;244(6):2442-2457. doi: 10.1111/nph.20181. Epub 2024 Oct 17. New Phytol. 2024. PMID: 39420761 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allers T., Lichten M. (2001). Differential timing and control of noncrossover and crossover recombination during meiosis. Cell 106: 47–57 - PubMed
-
- Armstrong S.J., Caryl A.P., Jones G.H., Franklin F.C. (2002). Asy1, a protein required for meiotic chromosome synapsis, localizes to axis-associated chromatin in Arabidopsis and Brassica. J. Cell Sci. 115: 3645–3655 - PubMed
-
- Baudat F., de Massy B. (2007). Regulating double-stranded DNA break repair towards crossover or non-crossover during mammalian meiosis. Chromosome Res. 15: 565–577 - PubMed
-
- Baumann P., Benson F.E., West S.C. (1996). Human Rad51 protein promotes ATP-dependent homologous pairing and strand transfer reactions in vitro. Cell 87: 757–766 - PubMed
-
- Bechtold N., Ellis J., Pelletier G. (1993). In planta Agrobacterium-mediated gene transfer by infiltration of adult Arabidopsis thaliana plants. Comptes Rendus Acad. Sci. Ser. Iii-Sciences De La Vie. Life Sciences. 316: 1194–1199
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

