Gastric endoscopic submucosal dissection: from animal model to patient
- PMID: 24363524
- PMCID: PMC3857456
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i45.8326
Gastric endoscopic submucosal dissection: from animal model to patient
Abstract
Aim: To assess whether the use of porcine models is useful for learning endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD), thus contributing to its subsequent application in human patients.
Methods: This study/learning process was carried out in 3 phases: Phase I: Ex vivo animal; Phase II: In vivo animal; Phase III: Humans. One endoscopist performed 30 gastric ESDs in porcine models, and later 5 gastric ESDs in 5 patients. The ESD was done following the method practiced at the National Cancer Center in Tokyo, Japan. Technical aspects, size, time and speed of ESD, as well as complications were registered. In patients, their clinical, endoscopic and histologic evolution was additionally added.
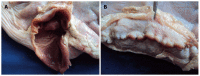
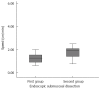
Results: Thirty en bloc ESDs were carried out in animal models. The mean ± SD size of the pieces was of 28.4 ± 1.2 mm, and the time of ESD was 41.7 ± 2.4 min. The time of ESD in the first 15 procedures was 43.0 ± 3.0 min whereas in the next 15 procedures, the time was 40.3 ± 3.9 min, P = 0.588. The speed in the first 15 ESDs was 1.25 ± 0.11 cm(2)/min vs 2.12 ± 0.36 cm(2)/min in the remaining 15, P = 0.028. There were no complications. In patients, 5 lesions were resected en bloc. The size of the pieces was 25.2 ± 5.1 mm and the time was 85.0 ± 25.6 min. Endoscopic and histological controls did not show evidence of residual neoplastic tissue.
Conclusion: A sequential ESD training program of a unique endoscopist, based on the practice in porcine models, contributed to learning ESD for its subsequent application in humans, yielding good results in efficacy and safety.
Keywords: Animal models; Endoscopic submucosal dissection; Porcine models; Training.
© 2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co., Limited. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Oyama T, Tomori A, Hotta K, Morita S, Kominato K, Tanaka M, Miyata Y. Endoscopic submucosal dissection of early esophageal cancer. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2005;3:S67–S70. - PubMed
-
- Yamamoto H. Endoscopic submucosal dissection of early cancers and large flat adenomas. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2005;3:S74–S76. - PubMed
-
- Muto M, Miyamoto S, Hosokawa A, Doi T, Ohtsu A, Yoshida S, Endo Y, Hosokawa K, Saito D, Shim CS, et al. Endoscopic mucosal resection in the stomach using the insulated-tip needle-knife. Endoscopy. 2005;37:178–182. - PubMed
-
- Gotoda T. Endoscopic resection for premalignant and malignant lesions of the gastrointestinal tract from the esophagus to the colon. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 2008;18:435–450, viii. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

