Dermal fillers in aesthetics: an overview of adverse events and treatment approaches
- PMID: 24363560
- PMCID: PMC3865975
- DOI: 10.2147/CCID.S50546
Dermal fillers in aesthetics: an overview of adverse events and treatment approaches
Abstract
Background: The ever-expanding range of dermal filler products for aesthetic soft tissue augmentation is of benefit for patients and physicians, but as indications and the number of procedures performed increase, the number of complications will likely also increase.
Objective: To describe potential adverse events associated with dermal fillers and to provide structured and clear guidance on their treatment and avoidance.
Methods: Reports of dermal filler complications in the medical literature were reviewed and, based on the publications retrieved and the authors' extensive experience, recommendations for avoiding and managing complications are provided.
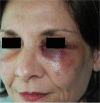
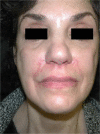
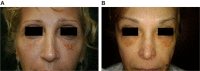
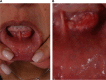
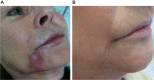
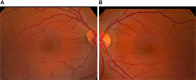
Results: Different dermal fillers have widely varying properties, associated risks, and injection requirements. All dermal fillers have the potential to cause complications. Most are related to volume and technique, though some are associated with the material itself. The majority of adverse reactions are mild and transient, such as bruising and trauma-related edema. Serious adverse events are rare, and most are avoidable with proper planning and technique.
Conclusion: For optimum outcomes, aesthetic physicians should have a detailed understanding of facial anatomy; the individual characteristics of available fillers; their indications, contraindications, benefits, and drawbacks; and ways to prevent and avoid potential complications.
Keywords: aesthetic medicine; complications.
Figures









References
-
- American Society for Aesthetic Plastic Surgery Cosmetic surgery national data bank statistics 2012. [Accessed September 13, 2013]. Available from: http://www.surgery.org/sites/default/fles/ASAPS-2011-Stats.pdf.
-
- Rzany B, Hilton S, Prager W, et al. Expert guideline on the use of porcine collagen in aesthetic medicine. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2010;8(3):210–217. - PubMed
-
- Goldberg DJ. Legal ramifications of off-label filler use. Dermatol Ther. 2006;19(3):189–193. - PubMed
-
- Glogau RG, Kane MA. Effect of injection techniques on the rate of local adverse events in patients implanted with nonanimal hyaluronic acid gel dermal fillers. Dermatol Surg. 2008;34(Suppl 1):S105–S109. - PubMed
-
- Zielke H, Wölber L, Wiest L, Rzany B. Risk profiles of different injectable fillers: results from the Injectable Filler Safety Study (IFS Study) Dermatol Surg. 2008;34(3):326–335. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

