The novel albumin-chitosan core-shell nanoparticles for gene delivery: preparation, optimization and cell uptake investigation
- PMID: 24363607
- PMCID: PMC3868460
- DOI: 10.1007/s11051-013-1651-0
The novel albumin-chitosan core-shell nanoparticles for gene delivery: preparation, optimization and cell uptake investigation
Abstract
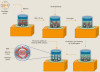
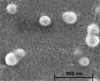
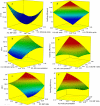
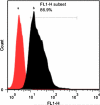
Natural polymers and proteins such as chitosan (CS) and albumin (Alb) have recently attracted much attention both in drug delivery and gene delivery. The underlying rationale is their unique properties such as biodegradability, biocompatibility and controlled release. This study aimed to prepare novel albumin-chitosan-DNA (Alb-CS-DNA) core-shell nanoparticles as a plasmid delivery system and find the best conditions for their preparation. Phase separation method and ionic interaction were used for preparation of Alb nanoparticles and Alb-CS-DNA core-shell nanoparticles, respectively. The effects of three important independent variables (1) CS/Alb mass ratio, (2) the ratios of moles of the amine groups of cationic polymers to those of the phosphate groups of DNA (N/P ratio), and (3) Alb concentration, on the nanoparticle size and loading efficiency of the plasmid were investigated and optimized through Box-Behnken design of response surface methodology (RSM). The optimum conditions were found to be CS/Alb mass ratio = 3, N/P ratio = 8.24 and Alb concentration = 0.1 mg/mL. The most critical factors for the size of nanoparticles and loading efficiency were Alb concentration and N/P ratio. The optimized nanoparticles had an average size of 176 ± 3.4 nm and loading efficiency of 80 ± 3.9 %. Cytotoxicity experiments demonstrated that the prepared nanoparticles were not toxic. The high cellular uptake of nanoparticles (~85 %) was shown by flow cytometry and fluorescent microscopy.
Keywords: Albumin; Chitosan; Gene delivery; Nanoparticle; Optimization.
Figures



References
-
- Arya G, Vandana M, Acharya S, Sahoo SK. Enhanced antiproliferative activity of Herceptin (HER2)-conjugated gemcitabine-loaded chitosan nanoparticle in pancreatic cancer therapy. Nanomedicine: Nanotechnology. Biology and Medicine. 2011;7(6):859–870. - PubMed
-
- Azarmi S, Tao X, Chen H, Wang Z, Finlay WH, Löbenberg R, Roa WH. Formulation and cytotoxicity of doxorubicin nanoparticles carried by dry powder aerosol particles. Int J Pharm. 2006;319(1–2):155–161. - PubMed
-
- Banerjee N, Krupanidhi SB. Facile hydrothermal synthesis and observation of bubbled growth mechanism in nano-ribbons aggregated microspherical Covellite blue-phosphor. Dalton Trans. 2010;39(41):9789–9793. - PubMed
-
- Bansal KK, Kakde D, Gupta U, Jain NK. Development and characterization of triazine based dendrimers for delivery of antitumor agent. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2010;10(12):8395–8404. - PubMed
-
- Che H-L, Muthiah M, Ahn Y, Son S, Kim WJ, Seonwoo H, Chung JH, Cho C-S, Park I-K. Biodegradable particulate delivery of vascular endothelial growth factor plasmid from polycaprolactone/polyethylenimine electrospun nanofibers for the treatment of myocardial infarction. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2011;11(8):7073–7077. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
