Etiology of non-traumatic acute abdomen in pediatric emergency departments
- PMID: 24364022
- PMCID: PMC3868711
- DOI: 10.12998/wjcc.v1.i9.276
Etiology of non-traumatic acute abdomen in pediatric emergency departments
Abstract
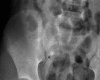
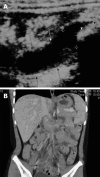
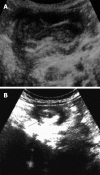
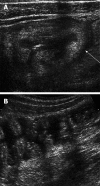
Acute abdominal pain is a common complaint in pediatric emergency departments. A complete evaluation is the key factor approaching the disease and should include the patient's age, any trauma history, the onset and chronicity of the pain, the related symptoms and a detailed physical examination. The aim of this review article is to provide some information for physicians in pediatric emergency departments, with the age factors and several causes of non-traumatic acute abdominal pain. The leading causes of acute abdominal pain are divided into four age groups: infants younger than 2 years old, children 2 to 5, children 5 to 12, and children older than 12 years old. We review the information about acute appendicitis, intussusception, Henoch-Schönlein purpura, infection, Meckel's diverticulum and mesenteric adenitis. In conclusion, the etiologies of acute abdomen in children admitted to the emergency department vary depending on age. A complete history and detailed physical examination, as well as abdominal imaging examinations, could provide useful information for physicians in the emergency department to narrow the differential diagnosis of abdominal emergencies and give a timely treatment.
Keywords: Abdominal pain; Non-traumatic acute abdominal pain.
Figures




References
-
- Andersson RE. Meta-analysis of the clinical and laboratory diagnosis of appendicitis. Br J Surg. 2004;91:28–37. - PubMed
-
- Andersson RE, Hugander A, Ravn H, Offenbartl K, Ghazi SH, Nyström PO, Olaison G. Repeated clinical and laboratory examinations in patients with an equivocal diagnosis of appendicitis. World J Surg. 2000;24:479–485; discussion 485. - PubMed
-
- Callahan MJ, Rodriguez DP, Taylor GA. CT of appendicitis in children. Radiology. 2002;224:325–332. - PubMed
-
- Lessin MS, Chan M, Catallozzi M, Gilchrist MF, Richards C, Manera L, Wallach MT, Luks FI. Selective use of ultrasonography for acute appendicitis in children. Am J Surg. 1999;177:193–196. - PubMed
-
- Rothrock SG, Pagane J. Acute appendicitis in children: emergency department diagnosis and management. Ann Emerg Med. 2000;36:39–51. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

