Synthesis, characterization, and acute oral toxicity evaluation of pH-sensitive hydrogel based on MPEG, poly(ε-caprolactone), and itaconic acid
- PMID: 24364030
- PMCID: PMC3864077
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/239838
Synthesis, characterization, and acute oral toxicity evaluation of pH-sensitive hydrogel based on MPEG, poly(ε-caprolactone), and itaconic acid
Abstract
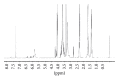
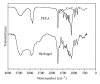
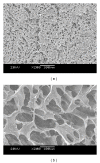
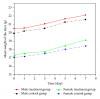
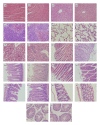
A kind of chemically cross-linked pH-sensitive hydrogels based on methoxyl poly(ethylene glycol)-poly(caprolactone)-acryloyl chloride (MPEG-PCL-AC, PECA), poly(ethylene glycol) methyl ether methacrylate (MPEGMA, MEG), N,N-methylenebisacrylamide (BIS), and itaconic acid (IA) were prepared without using any organic solvent by heat-initiated free radical method. The obtained macromonomers and hydrogels were characterized by ¹H NMR and FT-IR, respectively. Morphology study of hydrogels was also investigated in this paper, and it showed that the hydrogels had good pH-sensitivity. The acute toxicity test and histopathological study were conducted in BALB/c mice. The results indicated that the maximum tolerance dose of the hydrogel was higher than 10,000 mg/kg body weight. No morality or signs of toxicity were observed during the whole 7-day observation period. Compared to the control groups, there were no important adverse effects in the variables of hematology routine test and serum chemistry analysis both in male or female treatment group. Histopathological study also did not show any significant lesions, including heart, liver, lung, spleen, kidney, stomach, intestine, and testis. All the results demonstrated that this hydrogel was nontoxic after gavage. Thus, the hydrogel might be the biocompatible potential candidate for oral drug delivery system.
Figures


References
-
- Bromberg LE, Ron ES. Temperature-responsive gels and thermogelling polymer matrices for protein and peptide delivery. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews. 1998;31(3):197–221. - PubMed
-
- Zhang J, Chu L-Y, Li Y-K, Lee YM. Dual thermo- and pH-sensitive poly(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-acrylic acid) hydrogels with rapid response behaviors. Polymer. 2007;48(6):1718–1728.
-
- Qu X, Wirsén A, Albertsson A-C. Novel pH-sensitive chitosan hydrogels: swelling behavior and states of water. Polymer. 2000;41(12):4589–4598.
-
- Yeh PY, Kopečková P, Kopeček J. Biodegradable and pH-sensitive hydrogels: synthesis by crosslinking of N, N-dimethylacrylamide copolymer precursors. Journal of Polymer Science A. 2003;32(9):1627–1637.
-
- Wang T, Turhan M, Gunasekaran S. Selected properties of pH-sensitive, biodegradable chitosan-poly(vinyl alcohol) hydrogel. Polymer International. 2004;53(7):911–918.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

