Advances in the determination of nucleic acid conformational ensembles
- PMID: 24364917
- PMCID: PMC4748180
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev-physchem-040412-110059
Advances in the determination of nucleic acid conformational ensembles
Abstract
Conformational changes in nucleic acids play a key role in the way genetic information is stored, transferred, and processed in living cells. Here, we describe new approaches that employ a broad range of experimental data, including NMR-derived chemical shifts and residual dipolar couplings, small-angle X-ray scattering, and computational approaches such as molecular dynamics simulations to determine ensembles of DNA and RNA at atomic resolution. We review the complementary information that can be obtained from diverse sets of data and the various methods that have been developed to combine these data with computational methods to construct ensembles and assess their uncertainty. We conclude by surveying RNA and DNA ensembles determined using these methods, highlighting the unique physical and functional insights obtained so far.
Figures
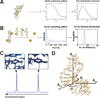

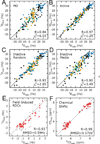
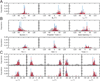

References
-
- Cruz JA, Westhof E. The dynamic landscapes of RNA architecture. Cell. 2009;136:604–609. - PubMed
-
- Fuxreiter M, Simon I, Bondos S. Dynamic protein-DNA recognition: beyond what can be seen. Trends Biochem Sci. 2011;36:415–423. - PubMed
-
- Perez A, Luque FJ, Orozco M. Frontiers in molecular dynamics simulations of DNA. Acc Chem Res. 2012;45:196–205. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

