Family members of patients with abdominal aortic aneurysms are at increased risk for aneurysms: analysis of 618 probands and their families from the Liège AAA Family Study
- PMID: 24365082
- PMCID: PMC4082690
- DOI: 10.1016/j.avsg.2013.11.005
Family members of patients with abdominal aortic aneurysms are at increased risk for aneurysms: analysis of 618 probands and their families from the Liège AAA Family Study
Abstract
Background: The objectives were to answer the following questions with the help of a well-characterized population in Liège, Belgium: 1) what percentage of patients with abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) have a positive family history for AAA? 2) what is the prevalence of AAAs among relatives of patients with AAA? and 3) do familial and sporadic AAA cases differ in clinical characteristics?
Methods: Patients with unrelated AAA diagnosed at the Cardiovascular Surgery Department, University Hospital of Liège, Belgium, between 1999 and 2012 were invited to the study. A detailed family history was obtained in interviews and recorded using Progeny software. We divided the 618 patients into 2 study groups: group I, 296 patients with AAA (268; 91% men) were followed up with computerized tomography combined with positron emission tomography; and group II, 322 patients with AAA (295; 92% men) whose families were invited to ultrasonographic screening.
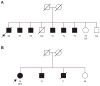
Results: In the initial interview, 62 (10%) of the 618 patients with AAA reported a positive family history for AAA. Ultrasonographic screening identified 24 new AAAs among 186 relatives (≥50 years) of 144 families yielding a prevalence of 13%. The highest prevalence (25%) was found among brothers. By combining the number of AAAs found by ultrasonographic screening with those diagnosed previously the observed lifetime prevalence of AAA was estimated to be 32% in brothers. The familial AAA cases were more likely to have a ruptured AAA than the sporadic cases (8% vs. 2.4%; P < 0.0001).
Conclusions: The findings confirm previously found high prevalence of AAA among brothers, support genetic contribution to AAA pathogenesis, and provide rationale for targeted screening of relatives of patients with AAA.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Sakalihasan N, Limet R, Defawe OD. Abdominal aortic aneurysm. Lancet. 2005;365:1577–1589. - PubMed
-
- Golledge J, Muller J, Daugherty A, Norman P. Abdominal aortic aneurysm: pathogenesis and implications for management. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2006;26:2605–2613. - PubMed
-
- Kuivaniemi H, Ryer EJ, Yoon YR, Elmore JR. Genetic risk factors for abdominal aortic aneurysms. In: Fischhof D, Hatig F, editors. Aortic Aneurysms: Risk Factors, Diagnosis, Surgery & Repair. New York: Nova Science Publishers; 2013. pp. 1–29.
-
- Kuivaniemi H, Tromp G, Carey DJ, Elmore JR. The Molecular Biology and Genetics of Aneurysms. In: Homeister JW, Willis MS, editors. Molecular and Translational Vascular Medicine. New York: Springer Science+Business Media; 2012. pp. 3–33.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

