Complementary functions of SK and Kv7/M potassium channels in excitability control and synaptic integration in rat hippocampal dentate granule cells
- PMID: 24366266
- PMCID: PMC3934708
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2013.267872
Complementary functions of SK and Kv7/M potassium channels in excitability control and synaptic integration in rat hippocampal dentate granule cells
Abstract
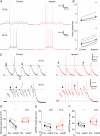
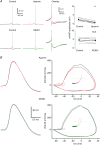
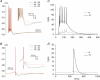
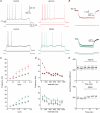
The dentate granule cells (DGCs) form the most numerous neuron population of the hippocampal memory system, and its gateway for cortical input. Yet, we have only limited knowledge of the intrinsic membrane properties that shape their responses. Since SK and Kv7/M potassium channels are key mechanisms of neuronal spiking and excitability control, afterhyperpolarizations (AHPs) and synaptic integration, we studied their functions in DGCs. The specific SK channel blockers apamin or scyllatoxin increased spike frequency (excitability), reduced early spike frequency adaptation, fully blocked the medium-duration AHP (mAHP) after a single spike or spike train, and increased postsynaptic EPSP summation after spiking, but had no effect on input resistance (Rinput) or spike threshold. In contrast, blockade of Kv7/M channels by XE991 increased Rinput, lowered the spike threshold, and increased excitability, postsynaptic EPSP summation, and EPSP-spike coupling, but only slightly reduced mAHP after spike trains (and not after single spikes). The SK and Kv7/M channel openers 1-EBIO and retigabine, respectively, had effects opposite to the blockers. Computational modelling reproduced many of these effects. We conclude that SK and Kv7/M channels have complementary roles in DGCs. These mechanisms may be important for the dentate network function, as CA3 neurons can be activated or inhibition recruited depending on DGC firing rate.
Figures






References
-
- Adams PR, Constanti A, Brown DA, Clark RB. Intracellular Ca2+ activates a fast voltage-sensitive K+ current in vertebrate sympathetic neurones. Nature. 1982;296:746–749. - PubMed
-
- Adams PR, Jones SW, Pennefather P, Brown DA, Koch C, Lancaster B. Slow synaptic transmission in frog sympathetic ganglia. J Exp Biol. 1986;124:259–285. - PubMed
-
- Adelman JP, Maylie J, Sah P. Small-conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channels: form and function. Annu Rev Physiol. 2012;74:245–269. - PubMed
-
- Alle H, Ostroumov K, Geiger J, Storm JF. Neuroscience Meeting Planner. Chicago, IL, USA: Society for Neuroscience; 2009. M-current, persistent Na+ current, and subthreshold resonance recorded in mossy fiber boutons (MFBs) in rat hippocampus. Program No. 42.2/D10. 2009 Online.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

