Neonatal severe bacterial infection impairment estimates in South Asia, sub-Saharan Africa, and Latin America for 2010
- PMID: 24366464
- PMCID: PMC3873707
- DOI: 10.1038/pr.2013.207
Neonatal severe bacterial infection impairment estimates in South Asia, sub-Saharan Africa, and Latin America for 2010
Abstract
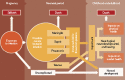
Background: Survivors of neonatal infections are at risk of neurodevelopmental impairment (NDI), a burden not previously systematically quantified and yet important for program priority setting. Systematic reviews and meta-analyses were undertaken and applied in a three-step compartmental model to estimate NDI cases after severe neonatal bacterial infection in South Asia, sub-Saharan Africa, and Latin America in neonates of >32 wk gestation (or >1,500 g).
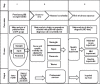
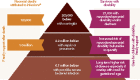
Methods: We estimated cases of sepsis, meningitis, pneumonia, or no severe bacterial infection from among estimated cases of possible severe bacterial infection ((pSBI) step 1). We applied respective case fatality risks ((CFRs) step 2) and the NDI risk among survivors (step 3). For neonatal tetanus, incidence estimates were based on the estimated deaths, CFRs, and risk of subsequent NDI.
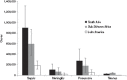
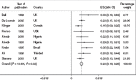
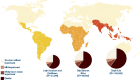
Results: For 2010, we estimated 1.7 million (uncertainty range: 1.1-2.4 million) cases of neonatal sepsis, 200,000 (21,000-350,000) cases of meningitis, 510,000 cases (150,000-930,000) of pneumonia, and 79,000 cases (70,000-930,000) of tetanus in neonates >32 wk gestation (or >1,500 g). Among the survivors, we estimated moderate to severe NDI after neonatal meningitis in 23% (95% confidence interval: 19-26%) of survivors, 18,000 (2,700-35,000) cases, and after neonatal tetanus in 16% (6-27%), 4,700 cases (1,700-8,900).
Conclusion: Data are lacking for impairment after neonatal sepsis and pneumonia, especially among those of >32 wk gestation. Improved recognition and treatment of pSBI will reduce neonatal mortality. Lack of follow-up data for survivors of severe bacterial infections, particularly sepsis, was striking. Given the high incidence of sepsis, even minor NDI would be of major public health importance. Prevention of neonatal infection, improved case management, and support for children with NDI are all important strategies, currently receiving limited policy attention.
Figures

References
-
- UNICEF. Levels and trends in child mortality. ( http://apromiserenewed.org/files/UNICEF_2012_child_mortality_for_web_090... .) Accessed 10 February 2013.
-
- Liu L, Johnson HL, Cousens S, et al. Child Health Epidemiology Reference Group of WHO and UNICEF Global, regional, and national causes of child mortality: an updated systematic analysis for 2010 with time trends since 2000. Lancet. 2012;379:2151–61. - PubMed
-
- Stoll BJ, Hansen NI, Adams-Chapman I, et al. National Institute of Child Health and Human Development Neonatal Research Network Neurodevelopmental and growth impairment among extremely low-birth-weight infants with neonatal infection. JAMA. 2004;292:2357–65. - PubMed
-
- Murray CJ, Vos T, Lozano R, et al. Disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) for 291 diseases and injuries in 21 regions, 1990-2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet. 2012;380:2197–223. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

