A novel CXCR3-B chemokine receptor-induced growth-inhibitory signal in cancer cells is mediated through the regulation of Bach-1 protein and Nrf2 protein nuclear translocation
- PMID: 24366869
- PMCID: PMC3916518
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M113.508044
A novel CXCR3-B chemokine receptor-induced growth-inhibitory signal in cancer cells is mediated through the regulation of Bach-1 protein and Nrf2 protein nuclear translocation
Erratum in
-
Correction: A novel CXCR3-B chemokine receptor-induced growth-inhibitory signal in cancer cells is mediated through the regulation of Bach-1 protein and Nrf2 protein nuclear translocation.J Biol Chem. 2020 Jul 24;295(30):10509. doi: 10.1074/jbc.AAC120.014986. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 32709763 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
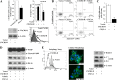
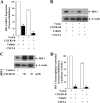
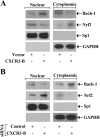
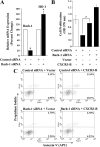
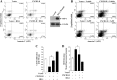
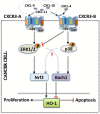
Chemokines and their receptors play diverse roles in regulating cancer growth and progression. The receptor CXCR3 can have two splice variants with opposite functions. CXCR3-A promotes cell growth, whereas CXCR3-B mediates growth-inhibitory signals. However, the negative signals through CXCR3-B in cancer cells are not well characterized. In this study, we found that CXCR3-B-mediated signaling in MCF-7 and T47D breast cancer cells induced apoptotic cell death. Signals through CXCR3-B decreased the levels of the antiapoptotic proteins Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL and increased the expression of apoptotic cleaved poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase. Along with up-regulation in apoptosis, CXCR3-B signals were associated with a decrease in cellular autophagy with reduced levels of the autophagic markers Beclin-1 and LC3B. Notably, CXCR3-B down-regulated the expression of the cytoprotective and antiapoptotic molecule heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) at the transcriptional level. There was an increased nuclear localization of Bach-1 and nuclear export of Nrf2, which are important negative and positive transcription factors, respectively, for HO-1 expression. We also observed that CXCR3-B promoted the activation of p38 MAPK and the inhibition of ERK-1/2. CXCR3-B could not induce cancer cell apoptosis at the optimal level when we either inhibited p38 activity or knocked down Bach-1. Further, CXCR3-B-induced apoptosis was down-regulated when we overexpressed HO-1. Together, our data suggest that CXCR3-B mediates a growth-inhibitory signal in breast cancer cells through the modulations of nuclear translocation of Bach-1 and Nrf2 and down-regulation of HO-1. We suggest that the induction of CXCR3-B-mediated signaling can serve as a novel therapeutic approach where the goal is to promote tumor cell apoptosis.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Chemokines; Heme Oxygenase; Nrf2; Nuclear Transport; Signal Transduction; Signaling.
Figures


References
-
- Zlotnik A., Yoshie O. (2000) Chemokines. A new classification system and their role in immunity. Immunity 12, 121–127 - PubMed
-
- Balkwill F., Mantovani A. (2001) Inflammation and cancer. Back to Virchow? Lancet 357, 539–545 - PubMed
-
- Vandercappellen J., Van Damme J., Struyf S. (2008) The role of CXC chemokines and their receptors in cancer. Cancer Lett. 267, 226–244 - PubMed
-
- Zipin-Roitman A., Meshel T., Sagi-Assif O., Shalmon B., Avivi C., Pfeffer R. M., Witz I. P., Ben-Baruch A. (2007) CXCL10 promotes invasion-related properties in human colorectal carcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 67, 3396–3405 - PubMed
-
- Walser T. C., Rifat S., Ma X., Kundu N., Ward C., Goloubeva O., Johnson M. G., Medina J. C., Collins T. L., Fulton A. M. (2006) Antagonism of CXCR3 inhibits lung metastasis in a murine model of metastatic breast cancer. Cancer Res. 66, 7701–7707 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

