Human Rev1 polymerase disrupts G-quadruplex DNA
- PMID: 24366879
- PMCID: PMC3950705
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkt1314
Human Rev1 polymerase disrupts G-quadruplex DNA
Abstract
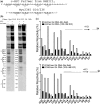
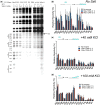
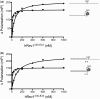
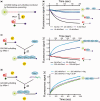
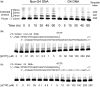
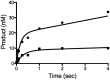
The Y-family DNA polymerase Rev1 is required for successful replication of G-quadruplex DNA (G4 DNA) in higher eukaryotes. Here we show that human Rev1 (hRev1) disrupts G4 DNA structures and prevents refolding in vitro. Nucleotidyl transfer by hRev1 is not necessary for mechanical unfolding to occur. hRev1 binds G4 DNA substrates with Kd,DNA values that are 4-15-fold lower than those of non-G4 DNA substrates. The pre-steady-state rate constant of deoxycytidine monophosphate (dCMP) insertion opposite the first tetrad-guanine by hRev1 is ∼56% as fast as that observed for non-G4 DNA substrates. Thus, hRev1 can promote fork progression by either dislodging tetrad guanines to unfold the G4 DNA, which could assist in extension by other DNA polymerases, or hRev1 can prevent refolding of G4 DNA structures. The hRev1 mechanism of action against G-quadruplexes helps explain why replication progress is impeded at G4 DNA sites in Rev1-deficient cells and illustrates another unique feature of this enzyme with important implications for genome maintenance.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Conservation of the insert-2 motif confers Rev1 from different species with an ability to disrupt G-quadruplexes and stimulate translesion DNA synthesis.RSC Chem Biol. 2023 May 11;4(7):466-485. doi: 10.1039/d3cb00027c. eCollection 2023 Jul 5. RSC Chem Biol. 2023. PMID: 37415867 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Twelve Germline Missense Variations on DNA Lesion and G-Quadruplex Bypass Activities of Human DNA Polymerase REV1.Chem Res Toxicol. 2016 Mar 21;29(3):367-79. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrestox.5b00513. Epub 2016 Mar 4. Chem Res Toxicol. 2016. PMID: 26914252 Free PMC article.
-
Human Rev1 relies on insert-2 to promote selective binding and accurate replication of stabilized G-quadruplex motifs.Nucleic Acids Res. 2021 Feb 26;49(4):2065-2084. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkab041. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021. PMID: 33555350 Free PMC article.
-
Mgs1 function at G-quadruplex structures during DNA replication.Curr Genet. 2021 Apr;67(2):225-230. doi: 10.1007/s00294-020-01128-1. Epub 2020 Nov 25. Curr Genet. 2021. PMID: 33237336 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cell cycle regulation of G-quadruplex DNA structures at telomeres.Curr Pharm Des. 2012;18(14):1867-72. doi: 10.2174/138161212799958404. Curr Pharm Des. 2012. PMID: 22376109 Review.
Cited by
-
G-quadruplex recognition and remodeling by the FANCJ helicase.Nucleic Acids Res. 2016 Oct 14;44(18):8742-8753. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw574. Epub 2016 Jun 24. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016. PMID: 27342280 Free PMC article.
-
Phase Separation Modulates the Formation and Stabilities of DNA Guanine Quadruplex.JACS Au. 2023 May 24;3(6):1650-1657. doi: 10.1021/jacsau.3c00106. eCollection 2023 Jun 26. JACS Au. 2023. PMID: 37388701 Free PMC article.
-
Conservation of the insert-2 motif confers Rev1 from different species with an ability to disrupt G-quadruplexes and stimulate translesion DNA synthesis.RSC Chem Biol. 2023 May 11;4(7):466-485. doi: 10.1039/d3cb00027c. eCollection 2023 Jul 5. RSC Chem Biol. 2023. PMID: 37415867 Free PMC article.
-
G4-Interacting DNA Helicases and Polymerases: Potential Therapeutic Targets.Curr Med Chem. 2019;26(16):2881-2897. doi: 10.2174/0929867324666171116123345. Curr Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 29149833 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Small-Molecule Inhibitor of Human DNA Polymerase η Potentiates the Effects of Cisplatin in Tumor Cells.Biochemistry. 2018 Feb 20;57(7):1262-1273. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.7b01176. Epub 2018 Jan 30. Biochemistry. 2018. PMID: 29345908 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Henderson E, Hardin CC, Walk SK, Tinoco I, Jr, Blackburn EH. Telomeric DNA oligonucleotides form novel intramolecular structures containing guanine-guanine base pairs. Cell. 1987;51:899–908. - PubMed
-
- Zahler AM, Williamson JR, Cech TR, Prescott DM. Inhibition of telomerase by G-quartet DNA structures. Nature. 1991;350:718–720. - PubMed
-
- Lipps HJ, Rhodes D. G-quadruplex structures: in vivo evidence and function. Trends Cell Biol. 2009;19:414–422. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

