Quantitative multiparametric MRI assessment of glioma response to radiotherapy in a rat model
- PMID: 24366911
- PMCID: PMC4022217
- DOI: 10.1093/neuonc/not245
Quantitative multiparametric MRI assessment of glioma response to radiotherapy in a rat model
Abstract
Background: The inability of structural MRI to accurately measure tumor response to therapy complicates care management for patients with gliomas. The purpose of this study was to assess the potential of several noninvasive functional and molecular MRI biomarkers for the assessment of glioma response to radiotherapy.
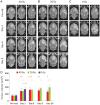
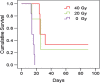
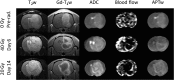
Methods: Fourteen U87 tumor-bearing rats were irradiated using a small-animal radiation research platform (40 or 20 Gy), and 6 rats were used as controls. MRI was performed on a 4.7 T animal scanner, preradiation treatment, as well as at 3, 6, 9, and 14 days postradiation. Image features of the tumors, as well as tumor volumes and animal survival, were quantitatively compared.
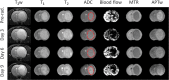
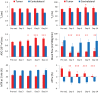
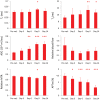
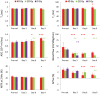
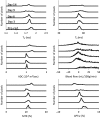
Results: Structural MRI showed that all irradiated tumors still grew in size during the initial days postradiation. The apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) values of tumors increased significantly postradiation (40 and 20 Gy), except at day 3 postradiation, compared with preradiation. The tumor blood flow decreased significantly postradiation (40 and 20 Gy), but the relative blood flow (tumor vs contralateral) did not show a significant change at most time points postradiation. The amide proton transfer weighted (APTw) signals of the tumor decreased significantly at all time points postradiation (40 Gy), and also at day 9 postradiation (20 Gy). The blood flow and APTw maps demonstrated tumor features that were similar to those seen on gadolinium-enhanced T1-weighted images.
Conclusions: Tumor ADC, blood flow, and APTw were all useful imaging biomarkers by which to predict glioma response to radiotherapy. The APTw signal was most promising for early response assessment in this model.
Keywords: APT imaging; glioma; multiparametric MRI; radiotherapy; response assessment.
© The Author(s) 2013. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Society for Neuro-Oncology. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
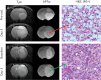
References
-
- Wen PY, Kesari S. Malignant gliomas in adults. N Engl J Med. 2008;359(5):492–507. - PubMed
-
- Walker MD, Alexander E, Jr., Hunt WE, et al. Evaluation of BCNU and/or radiotherapy in the treatment of anaplastic gliomas. A cooperative clinical trial. J Neurosurg. 1978;49(3):333–343. - PubMed
-
- Macdonald DR, Cascino TL, Schold SC, et al. Response criteria for phase II studies of supratentorial malignant glioma. J Clin Oncol. 1990;8(7):1277–1280. - PubMed
-
- Burger PC, Dubois PJ, Schold SC, Jr., et al. Computerized tomographic and pathologic studies of the untreated, quiescent, and recurrent glioblastoma multiforme. J Neurosurg. 1983;58(2):159–169. - PubMed
-
- Kumar AJ, Leeds NE, Fuller GN, et al. Malignant gliomas: MR imaging spectrum of radiation therapy- and chemotherapy-induced necrosis of the brain after treatment. Radiology. 2000;217(2):377–384. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

