Lapatinib: new opportunities for management of breast cancer
- PMID: 24367169
- PMCID: PMC3846530
- DOI: 10.2147/BCTT.S5929
Lapatinib: new opportunities for management of breast cancer
Abstract
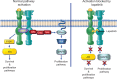
Approximately 20% of new diagnosed breast cancers overexpress the human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (EGFR2), also known as erythroblastic leukemia viral oncogene homolog 2 (ERBB2) protein, as a consequence of ERBB2 gene amplification, resulting in a poor prognosis. Clinical outcome can be substantially improved by ERBB2-targeted therapy. Lapatinib is a potent, orally bioavailable small molecule that reversibly and selectively inhibits epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR1 or ERBB1) and ERBB2 tyrosine kinases. Lapatinib binds the adenosine triphosphate-binding site of the receptor's intracellular domain to inhibit tumor cell growth. This review summarizes the pharmacology, pharmacokinetics, efficacy, and tolerability of lapatinib, and reviews both Food and Drug Administration-approved and investigational uses of lapatinib in breast cancer therapy. The drug is generally well tolerated in patients, with diarrhea and rashes being the most common (usually mild or moderate) adverse effects. Unlike trastuzumab, lapatinib has infrequent adverse effects on cardiac function. Lapatinib has substantial activity for advanced ERBB2-positive breast cancer, particularly in combination with capecitabine, following progression after anthracyclines, taxanes, and trastuzumab. Lapatinib combined with capecitabine yielded significant improvements in time to progression and response rate compared with capecitabine alone. This drug can also be combined with letrozole for the treatment of postmenopausal women with ERBB2-positive breast cancer, for whom hormonal therapy is indicated. Lapatinib has shown early promise in treatment of central nervous system metastasis and is being further evaluated in various clinical settings.
Keywords: ERBB family; ERBB2; breast cancer; capecitabine; lapatinib; letrozole; trastuzumab.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Lapatinib.Recent Results Cancer Res. 2018;211:19-44. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-91442-8_2. Recent Results Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 30069757 Review.
-
Lapatinib: a dual inhibitor of human epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinases.Clin Ther. 2008 Aug;30(8):1426-47. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2008.08.008. Clin Ther. 2008. PMID: 18803986 Review.
-
Lapatinib: a small-molecule inhibitor of epidermal growth factor receptor and human epidermal growth factor receptor-2 tyrosine kinases used in the treatment of breast cancer.Clin Ther. 2009;31 Pt 2:2332-48. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2009.11.029. Clin Ther. 2009. PMID: 20110044 Review.
-
[Lapatinib treatment-option in trastuzumab-resistant breast cancer].Magy Onkol. 2009 Dec;53(4):369-75. doi: 10.1556/MOnkol.53.2009.4.6. Magy Onkol. 2009. PMID: 20071309 Review. Hungarian.
-
Pyrotinib or Lapatinib Combined With Capecitabine in HER2-Positive Metastatic Breast Cancer With Prior Taxanes, Anthracyclines, and/or Trastuzumab: A Randomized, Phase II Study.J Clin Oncol. 2019 Oct 10;37(29):2610-2619. doi: 10.1200/JCO.19.00108. Epub 2019 Aug 20. J Clin Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31430226 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Novel Adamantanyl-Based Thiadiazolyl Pyrazoles Targeting EGFR in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer.ACS Omega. 2016 Dec 31;1(6):1412-1424. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.6b00251. Epub 2016 Dec 28. ACS Omega. 2016. PMID: 30023509 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative pharmacokinetics of tyrosine kinase inhibitor, lapatinib, in dogs and cats following single oral administration.J Vet Med Sci. 2024 Mar 16;86(3):317-321. doi: 10.1292/jvms.23-0448. Epub 2024 Jan 29. J Vet Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 38281758 Free PMC article.
-
A Validated RP-HPLC Method for the Estimation of Lapatinib in Tablet Dosage form using Gemcitabine Hydrochloride as an Internal Standard.Indian J Pharm Sci. 2012 Nov;74(6):580-3. doi: 10.4103/0250-474X.110621. Indian J Pharm Sci. 2012. PMID: 23798787 Free PMC article.
-
Androgen Receptor Expression in ER and PR Negative Breast Cancer-A Study from a Tertiary Hospital in Northern India.South Asian J Cancer. 2023 May 29;12(4):319-325. doi: 10.1055/s-0043-1768920. eCollection 2023 Oct. South Asian J Cancer. 2023. PMID: 38130277 Free PMC article.
-
PATRI, a Genomics Data Integration Tool for Biomarker Discovery.Biomed Res Int. 2018 Jun 28;2018:2012078. doi: 10.1155/2018/2012078. eCollection 2018. Biomed Res Int. 2018. PMID: 30065933 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J, Thun MJ. Cancer statistics, 2009. CA Cancer J Clin. 2009;59(4):225–249. - PubMed
-
- Chu I, Blackwell K, Chen S, Slingerland J. The dual ErbB1/ErbB2 inhibitor, lapatinib (GW572016), cooperates with tamoxifen to inhibit both cell proliferation- and estrogen-dependent gene expression in antiestrogen-resistant breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2005;65(1):18–25. - PubMed
-
- Tsutsui S, Ohno S, Murakami S, Hachitanda Y, Oda S. Prognostic value of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and its relationship to the estrogen receptor status in 1029 patients with breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2002;71(1):67–75. - PubMed
-
- Nicholson S, Wright C, Sainsbury JR, et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFr) as a marker for poor prognosis in node-negative breast cancer patients: Neu and tamoxifen failure. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 1990;37(6):811–814. - PubMed
-
- Agrawal A, Gutteridge E, Gee JM, Nicholson RI, Robertson JF. Overview of tyrosine kinase inhibitors in clinical breast cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2005;12(Suppl 1):S135–S144. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

