Delivery of continuously-varying stimuli using channelrhodopsin-2
- PMID: 24367294
- PMCID: PMC3853882
- DOI: 10.3389/fncir.2013.00184
Delivery of continuously-varying stimuli using channelrhodopsin-2
Abstract
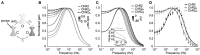
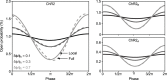
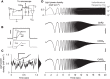
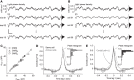
To study sensory processing, stimuli are delivered to the sensory organs of animals and evoked neural activity is recorded downstream. However, noise and uncontrolled modulatory input can interfere with repeatable delivery of sensory stimuli to higher brain regions. Here we show how channelrhodopsin-2 (ChR2) can be used to deliver continuous, subthreshold, time-varying currents to neurons at any point along the sensory-motor pathway. To do this, we first deduce the frequency response function of ChR2 using a Markov model of channel kinetics. We then confirm ChR2's frequency response characteristics using continuously-varying optical stimulation of neurons that express one of three ChR2 variants. We find that wild-type ChR2 and the E123T/H134R mutant ("CheTA") can pass continuously-varying subthreshold stimuli with frequencies up to ~70 Hz. Additionally, we find that wild-type ChR2 exhibits a strong resonance at ~6-10 Hz. Together, these results indicate that ChR2-derived optogenetic tools are useful for delivering highly repeatable artificial stimuli that mimic in vivo synaptic bombardment.
Keywords: channelrhodopsin-2; circuit dynamics; dynamical systems; electrophysiology methods; linear response theory; networks and dynamical systems; neural circuits; optogenetics.
Figures
References
-
- Arabzadeh E., Petersen R. S., Diamond M. E. (2003). Encoding of whisker vibration by rat barrel cortex neurons: implications for texture discrimination. J. Neurosci. 23, 9146–9154 Available online at: http://www.jneurosci.org/content/23/27/9146.full - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

