Xiangshao Granule Exerts Antidepressive Effects in a Depression Mouse Model by Ameliorating Deficits in Hippocampal BDNF and TrkB
- PMID: 24367385
- PMCID: PMC3866718
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/309262
Xiangshao Granule Exerts Antidepressive Effects in a Depression Mouse Model by Ameliorating Deficits in Hippocampal BDNF and TrkB
Abstract
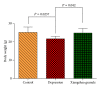
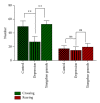
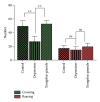
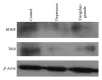
This study explores the therapeutic effects of Xiangshao granules in a mouse depression model and examines the potential molecular mechanisms involved. After 21 consecutive days of chronic stress challenge, all mice were divided into three groups: control group, depression group, and Xiangshao granule treatment group. On the 22nd day, rats in the Xiangshao granule treatment group received Xiangshao granules via gastrogavage for 3 consecutive weeks. Depression group mice showed a significant reduction of crossings (P < 0.01) but not rearings (P < 0.05). Serum CRH, CORT, and ACTH levels were significantly increased in depression mice compared with control (P < 0.05) and the expression levels of hippocampal BDNF and TrkB were reduced in the model group (P < 0.05). However, Xiangshao granule treatment remarkably rescued the decrease in the body weight (P < 0.05), increased crossings in the open field test (P < 0.05), upregulated the expression of hippocampal BDNF and TrkB expression, and reduced the serum CRH, CORT, and ACTH concentrations compared with the depression group (P < 0.05). Collectively, these results demonstrated that Xiangshao granule could effectively induce antidepressive effects in the depression mouse model by ameliorating the expression of hippocampal BDNF and TrkB.
Figures

References
-
- Propst AM, Quade BJ, Nowak RA, Stewart EA. Granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor in adenomyosis and autologous endometrium. Journal of the Society for Gynecologic Investigation. 2002;9(2):93–97. - PubMed
-
- Ge Q, Zhang H. Effects of Chinese herbal medicines for regulating liver qi on expression of 5-hydroxytryptamine 3B receptor in hypothalamic tissues of rats with anger emotion. Journal of Chinese Integrative Medicine. 2011;9(8):871–877. - PubMed
-
- Wang FR, Xue L, Zhang HY. Effects of xiangshao granule on mRNA and protein expression of mu opioid receptor in premenstrual syndrome gan-qi invasion rats. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 2012;32:1275–1279. - PubMed
-
- Jing Z, Yang X, Ismail KM, Chen X, Wu T. Chinese herbal medicine for premenstrual syndrome. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2009;(1)CD006414 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

