Biosynthesis of rare hexoses using microorganisms and related enzymes
- PMID: 24367410
- PMCID: PMC3869271
- DOI: 10.3762/bjoc.9.281
Biosynthesis of rare hexoses using microorganisms and related enzymes
Abstract
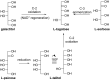
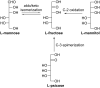
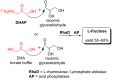
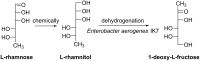
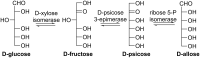
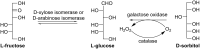
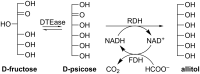
Rare sugars, referred to as monosaccharides and their derivatives that rarely exist in nature, can be applied in many areas ranging from foodstuffs to pharmaceutical and nutrition industry, or as starting materials for various natural products and drug candidates. Unfortunately, an important factor restricting the utilization of rare sugars is their limited availability, resulting from limited synthetic methods. Nowadays, microbial and enzymatic transformations have become a very powerful tool in this field. This article reviews the biosynthesis and enzymatic production of rare ketohexoses, aldohexoses and sugar alcohols (hexitols), including D-tagatose, D-psicose, D-sorbose, L-tagatose, L-fructose, 1-deoxy-L-fructose, D-allose, L-glucose, L-talose, D-gulose, L-galactose, L-fucose, allitol, D-talitol, and L-sorbitol. New systems and robust catalysts resulting from advancements in genomics and bioengineering are also discussed.
Keywords: biosynthesis; enzyme; hexose; microorganism; rare sugars.
Figures


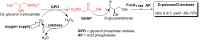
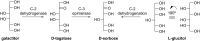

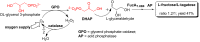


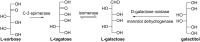



References
-
- Definition of rare sugars in 2011. and http://sites.google.com/site/raresugars/activity. Available from: http://isrs.kagawa-u.ac.jp/activities.html.
-
- Adibekian A, Stallforth P, Hecht M-L, Werz D B, Gagneux P, Seeberger P H. Chem Sci. 2011;2:337–344. doi: 10.1039/c0sc00322k. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
