Exposure to inflammatory cytokines IL-1β and TNFα induces compromise and death of astrocytes; implications for chronic neuroinflammation
- PMID: 24367648
- PMCID: PMC3868583
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0084269
Exposure to inflammatory cytokines IL-1β and TNFα induces compromise and death of astrocytes; implications for chronic neuroinflammation
Abstract
Background: Astrocytes have critical roles in the human CNS in health and disease. They provide trophic support to neurons and are innate-immune cells with keys roles during states-of-inflammation. In addition, they have integral functions associated with maintaining the integrity of the blood-brain barrier.
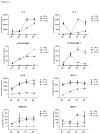
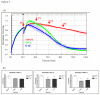
Methods: We have used cytometric bead arrays and xCELLigence technology to monitor the to monitor the inflammatory response profiles and astrocyte compromise in real-time under various inflammatory conditions. Responses were compared to a variety of inflammatory cytokines known to be released in the CNS during neuroinflammation. Astrocyte compromise measured by xCELLigence was confirmed using ATP measurements, cleaved caspase 3 expression, assessment of nuclear morphology and cell death.
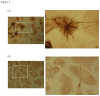
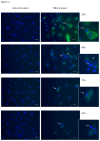
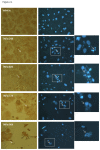
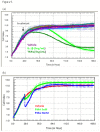
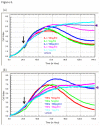
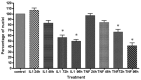
Results: Inflammatory activation (IL-1β or TNFα) of astrocytes results in the transient production of key inflammatory mediators including IL-6, cell surface adhesion molecules, and various leukocyte chemoattractants. Following this phase, the NT2-astrocytes progressively become compromised, which is indicated by a loss of adhesion, appearance of apoptotic nuclei and reduction in ATP levels, followed by DEATH. The earliest signs of astrocyte compromise were observed between 24-48 h post cytokine treatment. However, significant cell loss was not observed until at least 72 h, where there was also an increase in the expression of cleaved-caspase 3. By 96 hours approximately 50% of the astrocytes were dead, with many of the remaining showing signs of compromise too. Numerous other inflammatory factors were tested, however these effects were only observed with IL-1β or TNFα treatment.
Conclusions: Here we reveal direct sensitivity to mediators of the inflammatory milieu. We highlight the power of xCELLigence technology for revealing the early progressive compromise of the astrocytes, which occurs 24-48 hours prior to substantive cell loss. Death induced by IL-1β or TNFα is relevant clinically as these two cytokines are produced by various peripheral tissues and by resident brain cells.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Cartier L, Hartley O, Dubois-Dauphin M, Krause KH (2005) Chemokine receptors in the central nervous system: role in brain inflammation and neurodegenerative diseases. Brain research Brain research reviews 48: 16-42. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

