Incident chronic kidney disease and newly developed complications related to renal dysfunction in an elderly population during 5 years: a community-based elderly population cohort study
- PMID: 24367663
- PMCID: PMC3867482
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0084467
Incident chronic kidney disease and newly developed complications related to renal dysfunction in an elderly population during 5 years: a community-based elderly population cohort study
Abstract
Background: Few studies have evaluated the association between incident chronic kidney disease (CKD) and related complications, especially in elderly population. We attempted to verify the association between GFR and concurrent CKD complications and elucidate the temporal relationship between incident CKD and new CKD complications in a community-based prospective elderly cohort.
Method: We analyzed the available data from 984 participants in the Korean Longitudinal Study on Health and Aging. Participants were categorized into 6 groups according to eGFR at baseline examination (≥90, 75-89, 60-74, 45-59, 30-44, and <30 ml/min/1.73 m(2)).
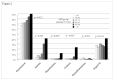
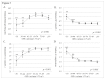
Result: The mean age of study population was 76 ± 9.1 years and mean eGFR was 72.3 ± 17.0 ml/min/1.73 m(2). Compared to eGFR group 1, the odds ratio (OR) for hypertension was 2.363 (95% CI, 1.299-4.298) in group 4, 5.191 (2.074-12.995) in group 5, and 13.675 (1.611-115.806) in group 6; for anemia, 7.842 (2.265-27.153) in group 5 and 13.019 (2.920-58.047) in group 6; for acidosis, 69.580 (6.770-715.147) in group 6; and for hyperkalemia, 19.177 (1.798-204.474) in group 6. Over a 5-year observational period, CKD developed in 34 (9.6%) among 354 participants with GFR ≥ 60 ml/min/1.73 m(2) at basal examination. The estimated mean number of new complications according to analysis of co-variance was 0.52 (95% CI, 0.35-0.68) in subjects with incident CKD and 0.24 (0.19-0.29) in subjects without CKD (p = 0.002). Subjects with incident CKD had a 2.792-fold higher risk of developing new CKD complications. A GFR level of 52.4 ml/min/1.73 m(2) (p = 0.032) predicted the development of a new CKD complication with a 90% sensitivity.
Conclusion: In an elderly prospective cohort, CKD diagnosed by current criteria is related to an increase in the number of concurrent CKD complications and the development of new CKD complications.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Bowling CB, Inker LA, Gutiérrez OM, Allman RM, Warnock DG et al. (2011) Age-specific associations of reduced estimated glomerular filtration rate with concurrent chronic kidney disease complications. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 6: 2822-2828. doi: 10.2215/CJN.06770711. PubMed: 22034504. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chin HJ, Song YR, Lee JJ, Lee SB, Kim KW et al. (2008) Moderately decreased renal function negatively affects the health-related quality of life among the elderly Korean population: a population-based study. Nephrol Dial Transplant 23: 2810-2817. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfn132. PubMed: 18372390. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

