Typical radiographic findings of dentin dysplasia type 1b with dental fluorosis
- PMID: 24367729
- PMCID: PMC3866844
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/902861
Typical radiographic findings of dentin dysplasia type 1b with dental fluorosis
Abstract
Dentin dysplasia is a rare inherited autosomal dominant disorder characterized by rootless teeth. We hereby report a case of dentin dysplasia type 1b with typical radiographic findings: short and blunt roots, pulpal obliteration, horizontal/crescent shaped radiolucencies in pulp chambers, and multiple periapical radiolucencies. However, the present case did not show the autosomal dominant pattern of inheritance and the patient also exhibited concurrent dental fluorosis, transposition of 13 and 14, and multiple cusps in maxillary first molars. Moreover, on careful review of previously documented cases of radiographs of dentin dysplasia, the horizontal/crescent shaped radiolucencies in pulp chambers are a rare finding, which is characteristically seen in the present case.
Figures

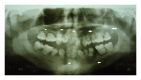
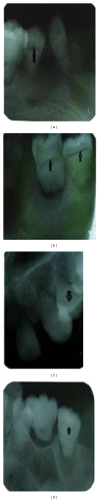
References
-
- Melnick M, Levin LS, Brady J. Dentin dysplasia type I: a scanning electron microscopic analysis of the primary dentition. Oral Surgery Oral Medicine and Oral Pathology. 1980;50(4):335–340. - PubMed
-
- Witkop CJ., Jr. Hereditary defects of dentin. Dental Clinics of North America. 1975;19(1):25–45. - PubMed
-
- Logan J, Becks H, Silverman S, Jr., Pindborg JJ. Dentinal dysplasia. Oral Surgery, Oral Medicine, Oral Pathology. 1962;15(3):317–333. - PubMed
-
- Carroll MKO, Duncan WK, Perkins TM. Dentin dysplasia: review of the literature and a proposed subclassification based on radiographic findings. Oral Surgery Oral Medicine and Oral Pathology. 1991;72(1):119–125. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

