JAK tyrosine kinases promote hierarchical activation of Rho and Rap modules of integrin activation
- PMID: 24368807
- PMCID: PMC3871442
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.201303067
JAK tyrosine kinases promote hierarchical activation of Rho and Rap modules of integrin activation
Abstract
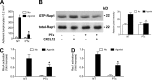
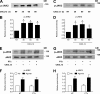
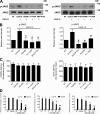
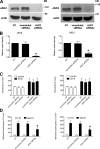
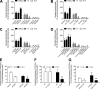
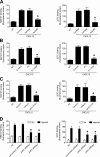
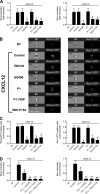
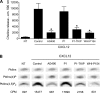
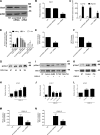
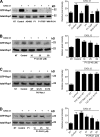
Lymphocyte recruitment is regulated by signaling modules based on the activity of Rho and Rap small guanosine triphosphatases that control integrin activation by chemokines. We show that Janus kinase (JAK) protein tyrosine kinases control chemokine-induced LFA-1- and VLA-4-mediated adhesion as well as human T lymphocyte homing to secondary lymphoid organs. JAK2 and JAK3 isoforms, but not JAK1, mediate CXCL12-induced LFA-1 triggering to a high affinity state. Signal transduction analysis showed that chemokine-induced activation of the Rho module of LFA-1 affinity triggering is dependent on JAK activity, with VAV1 mediating Rho activation by JAKs in a Gαi-independent manner. Furthermore, activation of Rap1A by chemokines is also dependent on JAK2 and JAK3 activity. Importantly, activation of Rap1A by JAKs is mediated by RhoA and PLD1, thus establishing Rap1A as a downstream effector of the Rho module. Thus, JAK tyrosine kinases control integrin activation and dependent lymphocyte trafficking by bridging chemokine receptors to the concurrent and hierarchical activation of the Rho and Rap modules of integrin activation.
Figures
References
-
- Battistini L., Piccio L., Rossi B., Bach S., Galgani S., Gasperini C., Ottoboni L., Ciabini D., Caramia M.D., Bernardi G., et al. 2003. CD8+ T cells from patients with acute multiple sclerosis display selective increase of adhesiveness in brain venules: a critical role for P-selectin glycoprotein ligand-1. Blood. 101:4775–4782 10.1182/blood-2002-10-3309 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bergmeier W., Goerge T., Wang H.W., Crittenden J.R., Baldwin A.C., Cifuni S.M., Housman D.E., Graybiel A.M., Wagner D.D. 2007. Mice lacking the signaling molecule CalDAG-GEFI represent a model for leukocyte adhesion deficiency type III. J. Clin. Invest. 117:1699–1707 10.1172/JCI30575 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

