Intricacies for posttranslational tumor-targeted cytokine gene therapy
- PMID: 24369443
- PMCID: PMC3863455
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/378971
Intricacies for posttranslational tumor-targeted cytokine gene therapy
Abstract
The safest and most effective cytokine therapies require the favorable accumulation of the cytokine in the tumor environment. While direct treatment into the neoplasm is ideal, systemic tumor-targeted therapies will be more feasible. Electroporation-mediated transfection of cytokine plasmid DNA including a tumor-targeting peptide-encoding sequence is one method for obtaining a tumor-targeted cytokine produced by the tumor-bearing patient's tissues. Here, the impact on efficacy of the location of targeting peptide, choice of targeting peptide, tumor histotype, and cytokine utilization are studied in multiple syngeneic murine tumor models. Within the same tumor model, the location of the targeting peptide could either improve or reduce the antitumor effect of interleukin (IL)12 gene treatments, yet in other tumor models the tumor-targeted IL12 plasmid DNAs were equally effective regardless of the peptide location. Similarly, the same targeting peptide that enhances IL12 therapies in one model fails to improve the effect of either IL15 or PF4 for inhibiting tumor growth in the same model. These interesting and sometimes contrasting results highlight both the efficacy and personalization of tumor-targeted cytokine gene therapies while exposing important aspects of these same therapies which must be considered before progressing into approved treatment options.
Figures



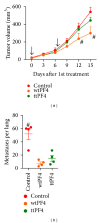

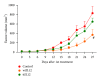
References
-
- Ko Y-J, Bubley GJ, Weber R, et al. Safety, pharmacokinetics, and biological pharmacodynamics of the immunocytokine EMD 273066 (huKS-IL2): results of a phase I trial in patients with prostate cancer. Journal of Immunotherapy. 2004;27(3):232–239. - PubMed
-
- Craig R, Cutrera J, Zhu S, Xia X, Lee Y-H, Li S. Administering plasmid DNA encoding tumor vessel-anchored IFN-α for localizing gene product within or into tumors. Molecular Therapy. 2008;16(5):901–906. - PubMed
-
- Atkins MB, Robertson MJ, Gordon M, et al. Phase I evaluation of intravenous recombinant human interleukin 12 in patients with advanced malignancies. Clinical Cancer Research. 1997;3(3):409–417. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

