Low-cytotoxic synthetic bromorutaecarpine exhibits anti-inflammation and activation of transient receptor potential vanilloid type 1 activities
- PMID: 24369537
- PMCID: PMC3863474
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/795095
Low-cytotoxic synthetic bromorutaecarpine exhibits anti-inflammation and activation of transient receptor potential vanilloid type 1 activities
Abstract
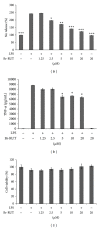
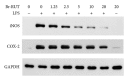
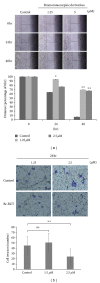
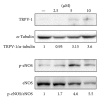
Rutaecarpine (RUT), the major bioactive ingredient isolated from the Chinese herb Evodia rutaecarpa, possesses a wide spectrum of biological activities, including anti-inflammation and preventing cardiovascular diseases. However, its high cytotoxicity hampers pharmaceutical development. We designed and synthesized a derivative of RUT, bromo-dimethoxyrutaecarpine (Br-RUT), which showed no cytotoxicity at 20 μM. Br-RUT suppressed nitric oxide (NO) production and tumor necrosis factor-α release in concentration-dependent (0~20 μM) manners in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-treated RAW 264.7 macrophages; protein levels of inducible NO synthase (iNOS) and cyclooxygenase-2 induced by LPS were downregulated. Br-RUT inhibited cell migration and invasion of ovarian carcinoma A2780 cells with 0~48 h of treatment. Furthermore, Br-RUT enhanced the expression of transient receptor potential vanilloid type 1 and activated endothelial NOS in human aortic endothelial cells. These results suggest that the synthetic Br-RUT possesses very low cytotoxicity but retains its activities against inflammation and vasodilation that could be beneficial for cardiovascular disease therapeutics.
Figures
References
-
- Liu Y-N, Pan S-L, Liao C-H, et al. Evodiamine represses hypoxia-induced inflammatory proteins expression and hypoxia-inducible factor 1α accumulation in RAW264.7. Shock. 2009;32(3):263–269. - PubMed
-
- Chiou W-F, Chou C-J, Shum AY-C, Chen C-F. The vasorelaxant effect of evodiamine in rat isolated mesenteric arteries: mode of action. European Journal of Pharmacology. 1992;215(2-3):277–283. - PubMed
-
- Chiou W-F, Shum AY-C, Liao J-F, Chen C-F. Studies of the cellular mechanisms underlying the vasorelaxant effects of rutaecarpine, a bioactive component extracted from an herbal drug. Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology. 1997;29(4):490–498. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

