Circulation of HIV-1 CRF02_AG among MSM population in central Italy: a molecular epidemiology-based study
- PMID: 24369538
- PMCID: PMC3863479
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/810617
Circulation of HIV-1 CRF02_AG among MSM population in central Italy: a molecular epidemiology-based study
Abstract
Introduction: The evolutionary and demographic history of the circular recombinant form CRF02_AG in a selected retrospective group of HIV-1 infected men who have sex with men (MSM) resident in Central Italy was investigated.
Methods: A total of 55 HIV-1 subtype CRF02_AG pol sequences were analyzed using Bayesian methods and a relaxed molecular clock to reconstruct their dated phylogeny and estimate population dynamics.
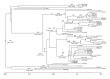
Results: Dated phylogeny indicated that the HIV-1 CRF02_AG strains currently circulating in Central Italy originated in the early 90's. Bayesian phylogenetic analysis revealed the existence of a main HIV-1 CRF02_AG clade, introduced in the area of Rome before 2000 and subsequently differentiated in two different subclades with a different date of introduction (2000 versus 2005). All the sequences within clusters were interspersed, indicating that the MSM analyzed form a close and restricted network where the individuals, also moving within different clinical centers, attend the same places to meet and exchange sex.
Conclusions: It was suggested that the HIV-1 CRF02_AG epidemic entered central Italy in the early 1990s, with a similar trend observed in western Europe.
Figures

References
-
- Barin F, Courouce A-M, Pillonel J, Buzelay L. Increasing diversity of HIV-1(M) serotypes in French blood donors over a 10-year period (1985–1995) AIDS. 1997;11(12):1503–1508. - PubMed
-
- Weidle PJ, Ganea CE, Irwin KL, et al. Presence of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) type 1, group M, non-B subtypes, Bronx, New York: a sentinel site for monitoring HIV genetic diversity in the United States. Journal of Infectious Diseases. 2000;181(2):470–475. - PubMed
-
- Yerly S, Vora S, Rizzardi P, et al. Acute HIV infection: impact on the spread of HIV and transmission of drug resistance. AIDS. 2001;15(17):2287–2292. - PubMed
-
- Holguín A, de Mulder M, Yebra G, López M, Soriano V. Increase of non-B subtypes and recombinants among newly diagnosed HIV-1 native spaniards and immigrants in Spain. Current HIV Research. 2008;6(4):327–334. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

