One-electron oxidation reactions of purine and pyrimidine bases in cellular DNA
- PMID: 24369822
- PMCID: PMC4047668
- DOI: 10.3109/09553002.2013.877176
One-electron oxidation reactions of purine and pyrimidine bases in cellular DNA
Abstract
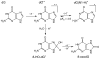
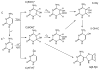
Purpose: The aim of this survey is to critically review the available information on one-electron oxidation reactions of nucleobases in cellular DNA with emphasis on damage induced through the transient generation of purine and pyrimidine radical cations. Since the indirect effect of ionizing radiation mediated by hydroxyl radical is predominant in cells, efforts have been made to selectively ionize bases using suitable one-electron oxidants that consist among others of high intensity UVC laser pulses. Thus, the main oxidation product in cellular DNA was found to be 8-oxo-7,8-dihydroguanine as a result of direct bi-photonic ionization of guanine bases and indirect formation of guanine radical cations through hole transfer reactions from other base radical cations. The formation of 8-oxo-7,8-dihydroguanine and other purine and pyrimidine degradation products was rationalized in terms of the initial generation of related radical cations followed by either hydration or deprotonation reactions in agreement with mechanistic pathways inferred from detailed mechanistic studies. The guanine radical cation has been shown to be implicated in three other nucleophilic additions that give rise to DNA-protein and DNA-DNA cross-links in model systems. Evidence was recently provided for the occurrence of these three reactions in cellular DNA.
Conclusion: There is growing evidence that one-electron oxidation reactions of nucleobases whose mechanisms have been characterized in model studies involving aqueous solutions take place in a similar way in cells. It may also be pointed out that the above cross-linked lesions are only produced from the guanine radical cation and may be considered as diagnostic products of the direct effect of ionizing radiation.
Keywords: DNA-protein cross-links; Ionizing radiation; intra and interstrand DNA cross-links; one-electron oxidation; oxidatively generated DNA damage.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest. The authors alone are responsible for the content and writing of the paper.
Figures
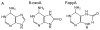


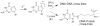
References
-
- Angelov D, Charra M, Müller CW, Cadet J, Dimitrov S. Solution study of the NF-kappa B p50-DNA complex by UV laser protein-DNA cross-linking. Photochem Photobiol. 2003;77:592–596. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
