Discriminative stimulus effects of nitrous oxide in mice: comparison with volatile hydrocarbons and vapor anesthetics
- PMID: 24370557
- PMCID: PMC3897127
- DOI: 10.1097/FBP.0000000000000017
Discriminative stimulus effects of nitrous oxide in mice: comparison with volatile hydrocarbons and vapor anesthetics
Abstract
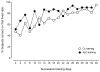
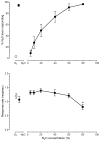
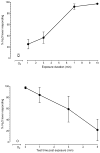
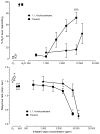
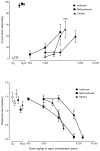
The abuse-related behavioral effects produced by nitrous oxide (N₂O) gas have been suggested as being unique compared with other abused inhalants. The drug discrimination paradigm in animals can be used to study subjective effects of drugs in humans and to test this hypothesis. The goals of the present experiment were to establish N₂O discrimination in mice and to compare its discriminative stimulus effects with those of abused volatile vapors and vapor anesthetics. Sixteen B6SJLF1/J mice were trained to discriminate between 10 min of exposure to 60% N₂O+40% oxygen (O₂) and 10 min of exposure to 100% O₂. The time course of N₂O discrimination was examined, followed by cross-substitution testing with abused vapors, volatile anesthetics, ethanol, D-amphetamine, and 2-butanol. Mice acquired the ability to discriminate between N₂O and O₂ in 40 days. N₂O fully substituted for 10 min of exposure to 60% N₂O in a concentration-dependent manner. Full substitution required 7 min of 60% N₂O exposure, but the offset of stimulus effects following the cessation of exposure was more rapid. The aromatic hydrocarbon toluene almost fully substituted for N₂O. 1,1,1-Trichloroethane, methoxyflurane, isoflurane, and ethanol showed lesser degrees of substitution. D-amphetamine and the odorant 2-butanol did not substitute for N₂O. Given the varying degrees of incomplete substitution by test compounds, the discriminative stimulus properties of N₂O and, perhaps, its subjective effects in humans are probably not unique. As none of the inhalants tested fully mimicked N₂O, its overall effects may include one or more novel stimulus components.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Discriminative stimulus effects of inhaled 1,1,1-trichloroethane in mice: comparison to other hydrocarbon vapors and volatile anesthetics.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2009 Apr;203(2):431-40. doi: 10.1007/s00213-008-1380-8. Epub 2008 Oct 30. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2009. PMID: 18972104 Free PMC article.
-
GABA(A) positive modulator and NMDA antagonist-like discriminative stimulus effects of isoflurane vapor in mice.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2010 Dec;212(4):559-69. doi: 10.1007/s00213-010-1979-4. Epub 2010 Aug 10. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2010. PMID: 20697696 Free PMC article.
-
Time course of the ethanol-like discriminative stimulus effects of abused inhalants in mice.Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2009 Jan;91(3):345-50. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2008.08.005. Epub 2008 Aug 8. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2009. PMID: 18722399 Free PMC article.
-
Discriminative Stimulus Effects of Abused Inhalants.Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2018;39:113-139. doi: 10.1007/7854_2016_22. Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 27714629 Review.
-
Drug Discrimination: Historical Origins, Important Concepts, and Principles.Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2018;39:3-26. doi: 10.1007/7854_2018_40. Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29637526 Review.
Cited by
-
N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor channel blocker-like discriminative stimulus effects of nitrous oxide gas.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2015 Jan;352(1):156-65. doi: 10.1124/jpet.114.218057. Epub 2014 Nov 3. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2015. PMID: 25368340 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abdullah W, Sheta S, Nooh N. Inhaled methoxyflurane (Penthrox) sedation for third molar extraction: a comparison to nitrous oxide sedation. Aust Dent J. 2011;56(3):296–301. - PubMed
-
- Balster R, Cruz S, Howard M, Dell C, Cottler L. Classification of abused inhalants. Addiction. 2009;104(6):878–882. - PubMed
-
- Balster R. Neural basis of inhalant abuse. Drug Alcohol Depend. 1998;51(1–2):207–214. - PubMed
-
- Beckman NJ, Zacny JP, Walker DJ. Within-subject comparison of the subjective and psychomotor effects of a gaseous anesthetic and two volatile anesthetics in healthy volunteers. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2006;81(1):89–95. - PubMed
-
- Bell D, McDonough J, Ellison J, Fitzhugh E. Controlled drug misuse by Certified Registered Nurse Anesthetists. AANA J. 1999;67(2):133–140. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

