The role of Ryk and Ror receptor tyrosine kinases in Wnt signal transduction
- PMID: 24370848
- PMCID: PMC3941236
- DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a009175
The role of Ryk and Ror receptor tyrosine kinases in Wnt signal transduction
Abstract
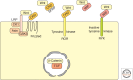
Receptor tyrosine kinases of the Ryk and Ror families were initially classified as orphan receptors because their ligands were unknown. They are now known to contain functional extracellular Wnt-binding domains and are implicated in Wnt-signal transduction in multiple species. Although their signaling mechanisms still remain to be resolved in detail, both Ryk and Ror control important developmental processes in different tissues. However, whereas many other Wnt-signaling responses affect cell proliferation and differentiation, Ryk and Ror are mostly associated with controlling processes that rely on the polarized migration of cells. Here we discuss what is currently known about the involvement of this exciting class of receptors in development and disease.
Figures
References
-
- Afzal AR, Jeffery S 2003. One gene, two phenotypes: ROR2 mutations in autosomal recessive Robinow syndrome and autosomal dominant brachydactyly type B. Hum Mutat 22: 1–11 - PubMed
-
- Afzal AR, Rajab A, Fenske CD, Oldridge M, Elanko N, Ternes-Pereira E, Tuysuz B, Murday VA, Patton MA, Wilkie AO, et al. 2000. Recessive Robinow syndrome, allelic to dominant brachydactyly type B, is caused by mutation of ROR2. Nat Genet 25: 419–422 - PubMed
-
- Al-Shawi R, Ashton SV, Underwood C, Simons JP 2001. Expression of the Ror1 and Ror2 receptor tyrosine kinase genes during mouse development. Dev Genes Evol 211: 161–171 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
