Converging pathways involving microRNA-206 and the RNA-binding protein KSRP control post-transcriptionally utrophin A expression in skeletal muscle
- PMID: 24371285
- PMCID: PMC3973319
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkt1350
Converging pathways involving microRNA-206 and the RNA-binding protein KSRP control post-transcriptionally utrophin A expression in skeletal muscle
Abstract
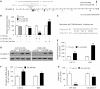
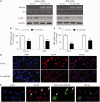
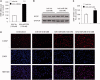
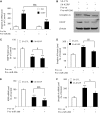
Several reports have previously highlighted the potential role of miR-206 in the post-transcriptional downregulation of utrophin A in cultured cells. Along those lines, we recently identified K-homology splicing regulator protein (KSRP) as an important negative regulator in the post-transcriptional control of utrophin A in skeletal muscle. We sought to determine whether these two pathways act together to downregulate utrophin A expression in skeletal muscle. Surprisingly, we discovered that miR-206 overexpression in cultured cells and dystrophic muscle fibers causes upregulation of endogenous utrophin A levels. We further show that this upregulation of utrophin A results from the binding of miR-206 to conserved sites located in the 3'-UTR (untranslated region) of KSRP, thus causing the subsequent inhibition of KSRP expression. This miR-206-mediated decrease in KSRP levels leads, in turn, to an increase in the expression of utrophin A due to a reduction in the activity of this destabilizing RNA-binding protein. Our work shows that miR-206 can oscillate between direct repression of utrophin A expression via its 3'-UTR and activation of its expression through decreased availability of KSRP and interactions with AU-rich elements located within the 3'-UTR of utrophin A. Our study thus reveals that two apparent negative post-transcriptional pathways can act distinctively as molecular switches causing repression or activation of utrophin A expression.
Figures




References
-
- Huntzinger E, Izaurralde E. Gene silencing by microRNAs: contributions of translational repression and mRNA decay. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2011;12:99–110. - PubMed
-
- Meister G. miRNAs get an early start on translational silencing. Cell. 2007;131:25–28. - PubMed
-
- Luo W, Nie Q, Zhang X. MicroRNAs involved in skeletal muscle differentiation. J. Genet. Genomics. 2013;40:107–116. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

