Botulinum protease-cleaved SNARE fragments induce cytotoxicity in neuroblastoma cells
- PMID: 24372287
- PMCID: PMC4063335
- DOI: 10.1111/jnc.12645
Botulinum protease-cleaved SNARE fragments induce cytotoxicity in neuroblastoma cells
Abstract
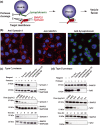
Soluble N-ethylmaleimide sensitive factor attachment protein receptors (SNAREs) are crucial for exocytosis, trafficking, and neurite outgrowth, where vesicular SNAREs are directed toward their partner target SNAREs: synaptosomal-associated protein of 25 kDa and syntaxin. SNARE proteins are normally membrane bound, but can be cleaved and released by botulinum neurotoxins. We found that botulinum proteases types C and D can easily be transduced into endocrine cells using DNA-transfection reagents. Following administration of the C and D proteases into normally refractory Neuro2A neuroblastoma cells, the SNARE proteins were cleaved with high efficiency within hours. Remarkably, botulinum protease exposures led to cytotoxicity evidenced by spectrophotometric assays and propidium iodide penetration into the nuclei. Direct delivery of SNARE fragments into the neuroblastoma cells reduced viability similar to botulinum proteases' application. We observed synergistic cytotoxic effects of the botulinum proteases, which may be explained by the release and interaction of soluble SNARE fragments. We show for the first time that previously observed cytotoxicity of botulinum neurotoxins/C in neurons could be achieved in cells of neuroendocrine origin with implications for medical uses of botulinum preparations. Ternary complex formation by synaptobrevin (green) and syntaxin/synaptosomal-associated protein of 25 kDa (red) is necessary for vesicle fusion, membrane trafficking, and cell homeostasis. Botulinum proteases cleave the three SNAREs proteins as indicated, resulting in a loss of cell viability. Lipofection reagents were used to deliver botulinum proteases or short SNARE peptides into neuroblastoma cells, revealing cytotoxic effects of SNARE fragments.
Keywords: SNARE; botulinum; cytotoxicity; neuro2A; syntaxin; transfection reagents.
© 2013 The Authors. Journal of Neurochemistry published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of International Society for Neurochemistry.
Figures




Comment in
-
A role for SNAREs in neuronal survival?J Neurochem. 2014 Jun;129(5):753-5. doi: 10.1111/jnc.12699. Epub 2014 Apr 2. J Neurochem. 2014. PMID: 24697239 No abstract available.
References
-
- Batcher E, Madaj P, Gianoukakis AG. Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. Endocr. Res. 2011;36:35–43. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

