Bulk segregant RNA-seq reveals expression and positional candidate genes and allele-specific expression for disease resistance against enteric septicemia of catfish
- PMID: 24373586
- PMCID: PMC3890627
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-14-929
Bulk segregant RNA-seq reveals expression and positional candidate genes and allele-specific expression for disease resistance against enteric septicemia of catfish
Abstract
Background: The application of RNA-seq has accelerated gene expression profiling and identification of gene-associated SNPs in many species. However, the integrated studies of gene expression along with SNP mapping have been lacking. Coupling of RNA-seq with bulked segregant analysis (BSA) should allow correlation of expression patterns and associated SNPs with the phenotypes.
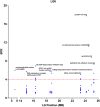
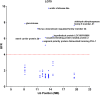
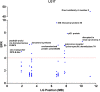
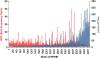
Results: In this study, we demonstrated the use of bulked segregant RNA-seq (BSR-Seq) for the analysis of differentially expressed genes and associated SNPs with disease resistance against enteric septicemia of catfish (ESC). A total of 1,255 differentially expressed genes were found between resistant and susceptible fish. In addition, 56,419 SNPs residing on 4,304 unique genes were identified as significant SNPs between susceptible and resistant fish. Detailed analysis of these significant SNPs allowed differentiation of significant SNPs caused by genetic segregation and those caused by allele-specific expression. Mapping of the significant SNPs, along with analysis of differentially expressed genes, allowed identification of candidate genes underlining disease resistance against ESC disease.
Conclusions: This study demonstrated the use of BSR-Seq for the identification of genes involved in disease resistance against ESC through expression profiling and mapping of significantly associated SNPs. BSR-Seq is applicable to analysis of genes underlining various performance and production traits without significant investment in the development of large genotyping platforms such as SNP arrays.
Figures





References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

