MicroRNAs affect BCL-2 family proteins in the setting of cerebral ischemia
- PMID: 24373752
- PMCID: PMC4071131
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuint.2013.12.006
MicroRNAs affect BCL-2 family proteins in the setting of cerebral ischemia
Abstract
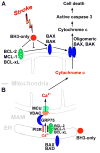
The BCL-2 family is centrally involved in the mechanism of cell death after cerebral ischemia. It is well known that the proteins of the BCL-2 family are key regulators of apoptosis through controlling mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization. Recent findings suggest that many BCL-2 family members are also directly involved in controlling transmission of Ca(2+) from the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) to mitochondria through a specialization called the mitochondria-associated ER membrane (MAM). Increasing evidence supports the involvement of microRNAs (miRNAs), some of them targeting BCL-2 family proteins, in the regulation of cerebral ischemia. In this mini-review, after highlighting current knowledge about the multiple functions of BCL-2 family proteins and summarizing their relationship to outcome from cerebral ischemia, we focus on the regulation of BCL-2 family proteins by miRNAs, especially miR-29 which targets multiple BCL-2 family proteins.
Keywords: BCL-2; Cerebral ischemia; Stroke; miR-29; microRNA.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicting financial interests.
Figures

References
-
- Bonneau B, Prudent J, Popgeorgiev N, Gillet G. Non-apoptotic roles of Bcl-2 family: the calcium connection. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013;1833:1755–1765. - PubMed
-
- Bonner HP, Concannon CG, Bonner C, Woods I, Ward MW, Prehn JH. Differential expression patterns of Puma and Hsp70 following proteasomal stress in the hippocampus are key determinants of neuronal vulnerability. J Neurochem. 2010;114:606–616. - PubMed
-
- Chami M, Prandini A, Campanella M, Pinton P, Szabadkai G, Reed JC, Rizzuto R. Bcl-2 and Bax exert opposing effects on Ca2+ signaling, which do not depend on their putative pore-forming region. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:54581–54589. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

