Tumor suppressor p53 and its mutants in cancer metabolism
- PMID: 24374014
- PMCID: PMC4069248
- DOI: 10.1016/j.canlet.2013.12.025
Tumor suppressor p53 and its mutants in cancer metabolism
Abstract
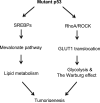
Tumor-suppressor p53 plays a key role in tumor prevention. As a transcription factor, p53 transcriptionally regulates its target genes to initiate different biological processes in response to stress, including apoptosis, cell cycle arrest or senescence, to exert its function in tumor suppression. Recent studies have revealed that metabolic regulation is a novel function of p53. Metabolic changes have been regarded as a hallmark of tumors and a key contributor to tumor development. p53 regulates many different aspects of metabolism, including glycolysis, mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation, pentose phosphate pathway, fatty acid synthesis and oxidation, to maintain the homeostasis of cellular metabolism, which contributes to the role of p53 in tumor suppression. p53 is frequently mutated in human tumors. In addition to loss of tumor suppressive function, tumor-associated mutant p53 proteins often gain new tumorigenic activities, termed gain-of-function of mutant p53. Recent studies have shown that mutant p53 mediates metabolic changes in tumors as a novel gain-of-function to promote tumor development. Here we review the functions and mechanisms of wild-type and mutant p53 in metabolic regulation, and discuss their potential roles in tumorigenesis.
Keywords: Metabolism; Mutant p53; Tumor suppressor; p53.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Vousden KH, Prives C. Blinded by the Light: The Growing Complexity of p53. Cell. 2009;137:413–431. - PubMed
-
- Olivier M, Hussain SP, Caron de Fromentel C, Hainaut P, Harris CC. TP53 mutation spectra and load: a tool for generating hypotheses on the etiology of cancer. IARC scientific publications. 2004:247–270. - PubMed
-
- Tommasino M, Accardi R, Caldeira S, Dong W, Malanchi I, Smet A, Zehbe I. The role of TP53 in Cervical carcinogenesis. Human mutation. 2003;21:307–312. - PubMed
-
- Scheffner M, Werness BA, Huibregtse JM, Levine AJ, Howley PM. The E6 oncoprotein encoded by human papillomavirus types 16 and 18 promotes the degradation of p53. Cell. 1990;63:1129–1136. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

