Lung uptake on I-131 therapy and short-term outcome in patients with lung metastasis from differentiated thyroid cancer
- PMID: 24374647
- PMCID: PMC3971446
- DOI: 10.1007/s12149-013-0781-x
Lung uptake on I-131 therapy and short-term outcome in patients with lung metastasis from differentiated thyroid cancer
Abstract
Objective: It is sometimes difficult to assess I-131 lung uptake at the initial I-131 therapy because of strong artifacts from I-131 uptake in the thyroid bed. The aim of this study was to analyze the lung uptake at the second I-131 therapy for lung metastasis in patients who did not have lung uptake at the initial therapy from differentiated thyroid carcinoma (DTC). Then, we also analyzed the relationship between the initial lung uptake and short-term outcome after I-131 therapies.
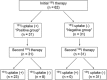
Methods: This study included 62 DTC patients with lung metastasis. The patients were classified into 2 groups according to the lung uptake at the initial I-131 therapy such as patients with lung uptake (positive uptake group n = 31) and those without lung uptake (negative uptake group n = 31). The lung uptake was analyzed at the second therapy in both groups. The short-term outcome was also analyzed based on the CT findings of lung metastasis size and serum thyroglobulin level between the two groups.
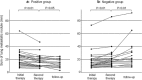
Results: The positive uptake group showed positive lung uptake at the second therapy in 23 patients (74 %), whereas none of negative uptake group showed any lung uptake at the second therapy (P < 0.01). The positive uptake group significantly decreased in the size of lung metastasis from the initial therapy to the second therapy (20.0 ± 11.7 to 16.6 ± 9.6 mm, P < 0.01) with further decrease after the second therapy (P < 0.05). The serum thyroglobulin level was also significantly decreased from the initial therapy to the second therapy (4348 ± 7011 to 2931 ± 4484 ng/ml, P < 0.05). In contrast, the negative uptake group significantly increased in the size of lung metastasis from the initial therapy to the second therapy (17.3 ± 12.2 to 19.9 ± 14.3 mm, P < 0.01) with further increase after the second therapy (P < 0.01).
Conclusion: No patients without lung uptake at the initial I-131 therapy showed lung uptake at the second therapy, or showed treatment effect. Therefore, second I-131 therapy for these patients with initially negative lung uptake should be considered cautiously.
Figures


References
-
- Casara D, Rubello D, Saladini G, Masarotto G, Favero A, Girelli ME, et al. Different features of pulmonary metastases in differentiated thyroid cancer: natural history and multivariate statistical analysis of prognostic variables. J Nucl Med. 1993;34:1626–1631. - PubMed
-
- Ronga G, Filesi M, Montesano T, Di Nicola AD, Pace C, Travascio L, et al. Lung metastases from differentiated thyroid carcinoma. A 40 years’ experience. Q J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2004;48:12–19. - PubMed
-
- Durante C, Haddy N, Baudin E, Leboulleux S, Hartl D, Travagli JP, et al. Long-term outcome of 444 patients with distant metastases from papillary and follicular thyroid carcinoma: benefits and limits of radioiodine therapy. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2006;91:2892–2899. doi: 10.1210/jc.2005-2838. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

