Interaction of valproic acid and the antidepressant drugs doxepin and venlafaxine: analysis of therapeutic drug monitoring data under naturalistic conditions
- PMID: 24374906
- PMCID: PMC4047312
- DOI: 10.1097/YIC.0000000000000025
Interaction of valproic acid and the antidepressant drugs doxepin and venlafaxine: analysis of therapeutic drug monitoring data under naturalistic conditions
Abstract
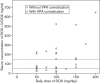
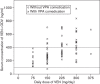
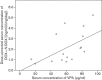
Valproic acid and the antidepressants doxepin and venlafaxine are frequently used psychotropic drugs. In the literature, an influence of valproic acid on serum levels of antidepressants has been described, although studies have focused on amitriptyline. The authors assessed their therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM) database for patients receiving a combination of doxepin or venlafaxine and valproic acid and compared these samples with matched controls without valproic acid comedication in terms of the serum concentration of antidepressants. The mean dose-corrected serum concentration of doxepin+N-doxepin in 16 patients who received valproic acid comedication was higher (2.171±1.482 ng/ml/mg) than that in the matched controls (0.971±0.857 ng/ml/mg, P<0.003). We also found a significant correlation between valproic acid serum level and dose-corrected doxepin+N-doxepin serum level (Spearman's ρ r=0.602, P<0.014). The mean dose-corrected serum level of venlafaxine+O-desmethylvenlafaxine in 41 patients who received valproic acid comedication did not differ significantly from that of the matched controls (P<0.089), but there was a significant difference between both groups in the dose-corrected serum level of O-desmethylvenlafaxine (1.403±0.665 vs. 1.102±0.444, P<0.017). As a consequence, if a combination of valproic acid with doxepin or venlafaxine is administered, cautious dosing is advisable and TDM should be performed.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Antidepressant polypharmacy and the potential of pharmacokinetic interactions: Doxepin but not mirtazapine causes clinically relevant changes in venlafaxine metabolism.J Affect Disord. 2018 Feb;227:506-511. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2017.11.046. Epub 2017 Nov 13. J Affect Disord. 2018. PMID: 29156365
-
Melperone is an inhibitor of the CYP2D6 catalyzed O-demethylation of venlafaxine.Pharmacopsychiatry. 2003 Jan;36(1):3-6. doi: 10.1055/s-2003-38084. Pharmacopsychiatry. 2003. PMID: 12649767
-
Interaction of valproic acid and amitriptyline: analysis of therapeutic drug monitoring data under naturalistic conditions.J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2013 Aug;33(4):561-4. doi: 10.1097/JCP.0b013e3182905d42. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23775047
-
Drug interactions and pharmacogenomics in the treatment of breast cancer and depression.Am J Psychiatry. 2008 Oct;165(10):1251-5. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2008.08040482. Am J Psychiatry. 2008. PMID: 18829880 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Antidepressant use in the elderly. Current status of nefazodone, venlafaxine and moclobemide.Drugs Aging. 1997 Aug;11(2):119-31. doi: 10.2165/00002512-199711020-00004. Drugs Aging. 1997. PMID: 9259175 Review.
Cited by
-
The Impact of Psychoactive Drugs on Seizures and Antiepileptic Drugs.Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2016 Aug;16(8):71. doi: 10.1007/s11910-016-0670-5. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27315249 Review.
-
Venlafaxine's therapeutic reference range in the treatment of depression revised: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2024 Feb;241(2):275-289. doi: 10.1007/s00213-023-06484-7. Epub 2023 Oct 19. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2024. PMID: 37857898 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacokinetic Interactions Between Antiseizure and Psychiatric Medications.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2023;21(8):1666-1690. doi: 10.2174/1570159X20666220524121645. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2023. PMID: 35611779 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amsterdam JD, Brunswick DJ.Antidepressant monotherapy for bipolar type II major depression.Bipolar Disord 2003;5:388–395 - PubMed
-
- Avoni P, Riva R, Albani F.Recurrence of absence seizures induced by a low dose of amitriptyline: a case report.Eur J Neurol 1996;3:272–274 - PubMed
-
- Bond DJ, Lam RW, Yatham LN.Divalproex sodium versus placebo in the treatment of acute bipolar depression: A systematic review and meta-analysis.J Affect Disord 2010;124:228–234 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

