HMGB1 is an early and critical mediator in an animal model of uveitis induced by IRBP-specific T cells
- PMID: 24374967
- PMCID: PMC3958740
- DOI: 10.1189/jlb.0613337
HMGB1 is an early and critical mediator in an animal model of uveitis induced by IRBP-specific T cells
Abstract
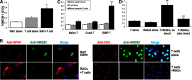
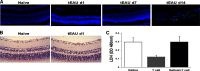
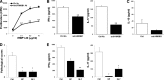
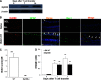
It is largely unknown how invading autoreactive T cells initiate the pathogenic process inside the diseased organ in organ-specific autoimmune disease. In this study, we used a chronic uveitis disease model in mice--EAU--induced by adoptive transfer of uveitogenic IRBP-specific T cells and showed that HMGB1, an important endogenous molecule that serves as a danger signal, was released rapidly from retinal cells into the ECM and intraocular fluid in response to IRBP-specific T cell transfer. HMGB1 release required direct cell-cell contact between retinal cells and IRBP-specific T cells and was an active secretion from intact retinal cells. Administration of HMGB1 antagonists inhibited severity of EAU significantly via mechanisms that include inhibition of IRBP-specific T cell proliferation and their IFN-γ and IL-17 production. The inflammatory effects of HMGB1 may signal the TLR/MyD88 pathway, as MyD88(-/-) mice had a high level of HMGB1 in the eye but did not develop EAU after IRBP-specific T cell transfer. Our study demonstrates that HMGB1 is an early and critical mediator of ocular inflammation initiated by autoreactive T cell invasion.
Keywords: autoimmune disease; autoreactive T cells; damage-associated molecular patterns; experimental autoimmune uveitis; immunoregulation; pathogen recognition receptors.
Figures



References
-
- Mochizuki M., Kuwabara T., McAllister C., Nussenblatt R. B., Gery I. (1985) Adoptive transfer of experimental autoimmune uveoretinitis in rats. Immunopathogenic mechanisms and histologic features. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 26, 1–9 - PubMed
-
- Chan C. C., Caspi R. R., Roberge F. G., Nussenblatt R. B. (1988) Dynamics of experimental autoimmune uveoretinitis induced by adoptive transfer of S-antigen-specific T cell line. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 29, 411–418 - PubMed
-
- Shao H., Liao T., Ke Y., Shi H., Kaplan H. J., Sun D. (2006) Severe chronic experimental autoimmune uveitis (EAU) of the C57BL/6 mouse induced by adoptive transfer of IRBP1–20-specific T cells. Exp. Eye Res. 82, 323–331 - PubMed
-
- Caspi R. R., Roberge F. G., McAllister C. G., el-Saied M., Kuwabara T., Gery I., Hanna E., Nussenblatt R. B. (1986) T cell lines mediating experimental autoimmune uveoretinitis (EAU) in the rat. J. Immunol. 136, 928–933 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

