Factors associated with bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome and chronic graft-versus-host disease after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation
- PMID: 24375545
- PMCID: PMC4314109
- DOI: 10.1002/ajh.23656
Factors associated with bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome and chronic graft-versus-host disease after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation
Abstract
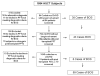
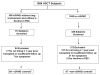
Bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome (BOS) is a form of chronic graft vs. host disease (cGVHD) and a highly morbid pulmonary complication after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT). We assessed the prevalence and risk factors for BOS and cGVHD in a cohort of HSCT recipients, including those who received reduced intensity conditioning (RIC) HSCT. Between January 1, 2000 and June 30, 2010, all patients who underwent allogeneic HSCT at our institution (n = 1854) were retrospectively screened for the development of BOS by PFT criteria. We matched the BOS cases with two groups of control patients: (1) patients who had concurrent cGVHD without BOS and (2) those who developed neither cGVHD nor BOS. Comparisons between BOS patients and controls were conducted using t-test or Fisher's exact tests. Multivariate regression analysis was performed to examine factors associated with BOS diagnosis. All statistical analyses were performed using SAS 9.2. We identified 89 patients (4.8%) meeting diagnostic criteria for BOS at a median time of 491 days (range: 48-2067) after HSCT. Eighty-six (97%) of our BOS cohort had extra-pulmonary cGVHD. In multivariate analysis compared to patients without cGVHD, patients who received busulfan-based conditioning, had unrelated donors, and had female donors were significantly more likely to develop BOS, while ATG administration was associated with a lower risk of BOS. Our novel results suggest that busulfan conditioning, even in RIC transplantation, could be an important risk factor for BOS and cGVHD.
Copyright © 2013 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Dudek A. Bronchiolitis obliterans in chronic graft-versus-host disease: analysis of risk factors and treatment outcomes. Biology of Blood and Marrow Transplantation. 2003;9:657–666. - PubMed
-
- Chien JW, Martin PJ, Gooley TA, Flowers ME, Heckbert SR, Nichols WG, Clark JG. Airflow obstruction after myeloablative allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine. 2003;168:208–214. - PubMed
-
- Clark JG, Schwartz DA, Flournoy N, Sullivan KM, Crawford SW, Thomas ED. Risk factors for airflow obstruction in recipients of bone marrow transplants. Annals of Internal Medicine. 1987;107:648–656. - PubMed
-
- Clark JG, Crawford SW, Madtes DK, Sullivan KM. Obstructive lung disease after allogeneic marrow transplantation. Clinical presentation and course. Annals of Internal Medicine. 1989;111:368–376. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P01 HL070149/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL091957/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL116473/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- CA142106/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL007118/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 5T32HL007118-35/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL107246-03/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL116473-01/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 5T32HL007680-20/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA142106/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K23HL089353-05/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL091957/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL007633/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 5T32HL007633-27/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01HL070149-02/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K23 HL089353/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL107246/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical