IL-12/Th1 and IL-23/Th17 biliary microenvironment in primary biliary cirrhosis: implications for therapy
- PMID: 24375552
- PMCID: PMC3999171
- DOI: 10.1002/hep.26979
IL-12/Th1 and IL-23/Th17 biliary microenvironment in primary biliary cirrhosis: implications for therapy
Abstract
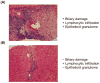
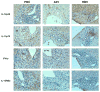
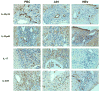
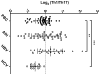
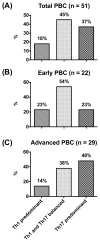
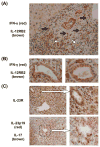
The interleukin (IL)-12/IL-23-mediated Th1/Th17 signaling pathway has been associated with the etiopathogenesis of primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC). To address the cytokine microenvironment specifically in the liver, we examined the localized expression of cytokine subunits and their corresponding receptors using previously optimized immunohistochemistry with an extensive panel of antibodies directed at IL-12p70, IL-12p35, interferon-gamma (IFN-γ), IL-12RB2, IL-23p40, IL-23p19, IL-17, and IL-23R using liver from PBC (n = 51) and non-PBC (n = 80) control liver disease patients. Multiple portal tracts in each patient were blindly evaluated and individually scored. We report herein that although IL-12/Th1 and IL-23/Th17 staining was detected in all of the liver sections, they were primarily localized around the damaged interlobular bile ducts in PBC. Most important, Th17 skewing was prominent in advanced PBC patients with intensive secretion of IL-23p19 by inflamed hepatocytes around IL-23R, IL-12RB2, and IFN-γ expressing degenerated cholangiocytes. Our novel finding on the direct association of Th17 skewing and disease severity illustrates the significance of the IL-23/Th17 pathway in the perpetuation of IL-12/Th1-mediated immunopathology in PBC. Furthermore, localized IL-23p19 production by hepatocytes may enhance profibrotic Th17 signaling and proinflammatory IFN-γ production that contribute to PBC pathology.
Conclusion: Our data emphasize the pathogenic relevance of IL-12/Th1 and IL-23/Th17 in the evolution of PBC. Of significance, however, the shift from a Th1 to a Th17 imbalance at advanced stages of the disease suggests the necessity to consider modulation of the IL-23/Th17 pathway as a potential target for therapeutic intervention.
© 2014 by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
