Transglutaminase 2-mediated serotonylation in pulmonary hypertension
- PMID: 24375797
- PMCID: PMC3920225
- DOI: 10.1152/ajplung.00321.2013
Transglutaminase 2-mediated serotonylation in pulmonary hypertension
Abstract
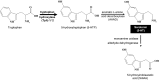
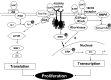
The monoamine serotonin (5-HT) has been previously implicated in pulmonary arterial remodeling and is considered a potential therapeutic target for the disease pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH). More recently, it has been recognized that the enzyme tissue transglutaminase (TG2) mediates cross-linking of proteins with 5-HT, a posttranslational process of monoaminylation known as "serotonylation." TG2 activity and serotonylation of protein participate in both smooth muscle proliferation and contraction produced by 5-HT. Indeed, markedly increased TG2 activity has now been identified in lung tissue of an experimental rodent model of pulmonary hypertension, and elevated serotonylation of fibronectin and the signaling molecule Rho, downstream products of transglutamidation, have been found in blood of patients with PAH. The basic mechanism by which TG2 is activated and the potential role(s) of serotonylated proteins in pulmonary hypertension remain a mystery. In the present review we have tried to address the current understanding of 5-HT metabolism in pulmonary hypertension and relate it to what is currently known about the evolving cellular process of serotonylation.
Keywords: pulmonary hypertension; serotonin; serotonylation; transglutamidation; transglutaminase 2.
Figures
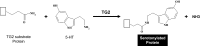
Similar articles
-
Serotonylation: Serotonin Signaling and Epigenetics.Front Mol Neurosci. 2019 Nov 21;12:288. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2019.00288. eCollection 2019. Front Mol Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31824263 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of hypoxia-induced transglutaminase 2 in pulmonary artery smooth muscle cell proliferation.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2014 Oct 1;307(7):L576-85. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00162.2014. Epub 2014 Aug 15. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2014. PMID: 25128524 Free PMC article.
-
Tissue transglutaminase promotes serotonin-induced AKT signaling and mitogenesis in pulmonary vascular smooth muscle cells.Cell Signal. 2014 Dec;26(12):2818-25. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2014.09.002. Epub 2014 Sep 15. Cell Signal. 2014. PMID: 25218191 Free PMC article.
-
RhoA and Rho kinase activation in human pulmonary hypertension: role of 5-HT signaling.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2009 Jun 15;179(12):1151-8. doi: 10.1164/rccm.200805-691OC. Epub 2009 Mar 19. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2009. PMID: 19299501
-
Serotonylation and Transamidation of Other Monoamines.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2015 Jul 15;6(7):961-9. doi: 10.1021/cn500329r. Epub 2015 Feb 5. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25615632 Review.
Cited by
-
Microvessel mechanobiology in pulmonary arterial hypertension: cause and effect.Hypertension. 2015 Mar;65(3):483-9. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.114.04652. Epub 2014 Dec 22. Hypertension. 2015. PMID: 25534705 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Mitochondrial dysfunction and pulmonary hypertension: cause, effect, or both.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2018 May 1;314(5):L782-L796. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00331.2017. Epub 2018 Jan 18. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29345195 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lung-specific interleukin 6 mediated transglutaminase 2 activation and cardiopulmonary fibrogenesis.Front Immunol. 2024 Apr 8;15:1371706. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1371706. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38650935 Free PMC article.
-
Serotonylation: Serotonin Signaling and Epigenetics.Front Mol Neurosci. 2019 Nov 21;12:288. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2019.00288. eCollection 2019. Front Mol Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31824263 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of hypoxia-induced transglutaminase 2 in pulmonary artery smooth muscle cell proliferation.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2014 Oct 1;307(7):L576-85. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00162.2014. Epub 2014 Aug 15. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2014. PMID: 25128524 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abenhaim L, Moride Y, Brenot F, Rich S, Benichou J, Kurz X, Higenbottam T, Oakley C, Wouters E, Aubier M, Simonneau G, Begaud B. Appetite-suppressant drugs and the risk of primary pulmonary hypertension. International Primary Pulmonary Hypertension Study Group. N Engl J Med 335: 609–616, 1996 - PubMed
-
- Abid S, Houssaini A, Chevarin C, Marcos E, Tissot CM, Gary-Bobo G, Wan F, Mouraret N, Amsellem V, Dubois-Rande JL, Hamon M, Adnot S. Inhibition of gut- and lung-derived serotonin attenuates pulmonary hypertension in mice. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 303: L500–L508, 2012 - PubMed
-
- Achyuthan KE, Greenberg CS. Identification of a guanosine triphosphate-binding site on guinea pig liver transglutaminase. Role of GTP and calcium ions in modulating activity. J Biol Chem 262: 1901–1906, 1987 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

