Ectopic Ptf1a expression in murine ESCs potentiates endocrine differentiation and models pancreas development in vitro
- PMID: 24375815
- PMCID: PMC4283475
- DOI: 10.1002/stem.1616
Ectopic Ptf1a expression in murine ESCs potentiates endocrine differentiation and models pancreas development in vitro
Abstract
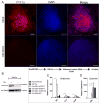
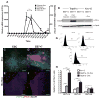
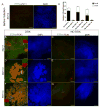
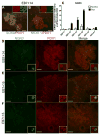
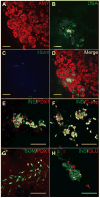
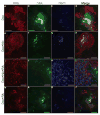
Besides its role in exocrine differentiation, pancreas-specific transcription factor 1a (PTF1a) is required for pancreas specification from the foregut endoderm and ultimately for endocrine cell formation. Examining the early role of PTF1a in pancreas development has been challenging due to limiting amounts of embryonic tissue material for study. Embryonic stem cells (ESCs) which can be differentiated in vitro, and without limit to the amount of experimental material, can serve as a model system to study these early developmental events. To this end, we derived and characterized a mouse ESC line with tetracycline-inducible expression of PTF1a (tet-Ptf1a mESCs). We found that transient ectopic expression of PTF1a initiated the pancreatic program in differentiating ESCs causing cells to activate PDX1 expression in bud-like structures resembling pancreatic primordia in vivo. These bud-like structures also expressed progenitor markers characteristic of a developing pancreatic epithelium. The epithelium differentiated to generate a wave of NGN3+ endocrine progenitors, and further formed cells of all three pancreatic lineages. Notably, the insulin+ cells in the cultures were monohormonal, and expressed PDX1 and NKX6.1. PTF1a-induced cultures differentiated into significantly more endocrine and exocrine cells and the ratio of endocrine-to-exocrine cell differentiation could be regulated by retinoic acid (RA) and nicotinamide (Nic) signaling. Moreover, induced cultures treated with RA and Nic exhibited a modest glucose response. Thus, this tet-Ptf1a ESC-based in vitro system is a valuable new tool for interrogating the role of PTF1a in pancreas development and in directing differentiation of ESCs to endocrine cells.
Keywords: Acinar morphology; Beta cells; Embryonic stem cells; Endocrine; Insulin; Neurogenin3; Pancreas development; Pancreatic duodenal homeobox 1; Pluripotent stem cells; Ptf1a.
© 2013 AlphaMed Press.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest directly related to the subject matter of the manuscript.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Ptf1a function and transcriptional cis-regulation, a cornerstone in vertebrate pancreas development.FEBS J. 2022 Sep;289(17):5121-5136. doi: 10.1111/febs.16075. Epub 2021 Jun 30. FEBS J. 2022. PMID: 34125483 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterization of an in vitro differentiation assay for pancreatic-like cell development from murine embryonic stem cells: detailed gene expression analysis.Assay Drug Dev Technol. 2011 Aug;9(4):403-19. doi: 10.1089/adt.2010.0314. Epub 2011 Mar 11. Assay Drug Dev Technol. 2011. PMID: 21395400 Free PMC article.
-
Pdx-1 and Ptf1a concurrently determine fate specification of pancreatic multipotent progenitor cells.Dev Biol. 2008 Apr 1;316(1):74-86. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2008.01.011. Epub 2008 Jan 26. Dev Biol. 2008. PMID: 18294628 Free PMC article.
-
Exdpf is a key regulator of exocrine pancreas development controlled by retinoic acid and ptf1a in zebrafish.PLoS Biol. 2008 Nov 25;6(11):e293. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0060293. PLoS Biol. 2008. PMID: 19067490 Free PMC article.
-
Genes controlling pancreas ontogeny.Int J Dev Biol. 2008;52(7):823-35. doi: 10.1387/ijdb.072444cb. Int J Dev Biol. 2008. PMID: 18956314 Review.
Cited by
-
β-Cell Replacement Strategies: The Increasing Need for a "β-Cell Dogma".Front Genet. 2017 Jun 6;8:75. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2017.00075. eCollection 2017. Front Genet. 2017. PMID: 28634486 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protein Methyltransferase Inhibition Decreases Endocrine Specification Through the Upregulation of Aldh1b1 Expression.Stem Cells. 2019 May;37(5):640-651. doi: 10.1002/stem.2979. Epub 2019 Feb 13. Stem Cells. 2019. PMID: 30681750 Free PMC article.
-
Expression and clinicopathological characteristics of PDX1, PTF1A, and SALL4 in large and small ducts of ectopic pancreas located in gastro-duodenum and jejunum.Heliyon. 2023 Jul 13;9(7):e18241. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e18241. eCollection 2023 Jul. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37519669 Free PMC article.
-
Ptf1a function and transcriptional cis-regulation, a cornerstone in vertebrate pancreas development.FEBS J. 2022 Sep;289(17):5121-5136. doi: 10.1111/febs.16075. Epub 2021 Jun 30. FEBS J. 2022. PMID: 34125483 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multiscale 3D genome rewiring during PTF1A-mediated somatic cell reprogramming into neural stem cells.Commun Biol. 2024 Nov 14;7(1):1505. doi: 10.1038/s42003-024-07230-1. Commun Biol. 2024. PMID: 39537822 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kawaguchi Y, Cooper B, Gannon M, et al. The role of the transcriptional regulator Ptf1a in converting intestinal to pancreatic progenitors. Nat Genet. 2002;32(1):128–134. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

