Subtilase SprP exerts pleiotropic effects in Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- PMID: 24376018
- PMCID: PMC3937732
- DOI: 10.1002/mbo3.150
Subtilase SprP exerts pleiotropic effects in Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Abstract
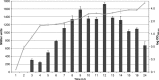
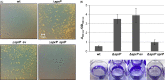
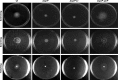
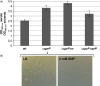
The open reading frame PA1242 in the genome of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 encodes a putative protease belonging to the peptidase S8 family of subtilases. The respective enzyme termed SprP consists of an N-terminal signal peptide and a so-called S8 domain linked by a domain of unknown function (DUF). Presumably, this DUF domain defines a discrete class of Pseudomonas proteins as homologous domains can be identified almost exclusively in proteins of the genus Pseudomonas. The sprP gene was expressed in Escherichia coli and proteolytic activity was demonstrated. A P. aeruginosa ∆sprP mutant was constructed and its gene expression pattern compared to the wild-type strain by genome microarray analysis revealing altered expression levels of 218 genes. Apparently, SprP is involved in regulation of a variety of different cellular processes in P. aeruginosa including pyoverdine synthesis, denitrification, the formation of cell aggregates, and of biofilms.
Keywords: Biofilm; Pseudomonas aeruginosa; Pyoverdine.; microarray; motility; orf PA1242; protease.
© 2013 The Authors. MicrobiologyOpen published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures



References
-
- Alexeyev MF, Shokolenko IN, Croughan TP. Improved antibiotic-resistance gene cassettes and omega elements for Escherichia coli vector construction and in vitro deletion/insertion mutagenesis. Gene. 1995;160:63–67. - PubMed
-
- Antao CM, Malcata FX. Plant serine proteases: biochemical, physiological and molecular features. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2005;43:637–650. - PubMed
-
- Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y. Controlling the fasle discovery rate – a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J. Roy. Stat. Soc. 1995;57:289–300.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

