B cell-specific loss of Lyn kinase leads to autoimmunity
- PMID: 24376269
- PMCID: PMC3900234
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1301979
B cell-specific loss of Lyn kinase leads to autoimmunity
Abstract
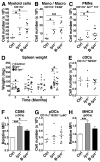
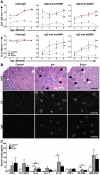
The Lyn tyrosine kinase regulates inhibitory signaling in B and myeloid cells: loss of Lyn results in a lupus-like autoimmune disease with hyperactive B cells and myeloproliferation. We have characterized the relative contribution of Lyn-regulated signaling pathways in B cells specifically to the development of autoimmunity by crossing the novel lyn(flox/flox) animals with mice carrying the Cre recombinase under the control of the Cd79a promoter, resulting in deletion of Lyn in B cells. The specific deletion of Lyn in B cells is sufficient for the development of immune complex-mediated glomerulonephritis. The B cell-specific Lyn-deficient mice have no defects in early bone marrow B cell development but have reduced numbers of mature B cells with poor germinal centers, as well as increased numbers of plasma and B1a cells, similar to the lyn(-/-) animals. Within 8 mo of life, B cell-specific Lyn mutant mice develop high titers of IgG anti-Smith Ag ribonucleoprotein and anti-dsDNA autoantibodies, which deposit in their kidneys, resulting in glomerulonephritis. B cell-specific Lyn mutant mice also develop myeloproliferation, similar to the lyn(-/-) animals. The additional deletion of MyD88 in B cells, achieved by crossing lyn(flox/flox)Cd79a-cre mice with myd88(flox/flox) animals, reversed the autoimmune phenotype observed in B cell-specific Lyn-deficient mice by blocking production of class-switched pathogenic IgG autoantibodies. Our results demonstrate that B cell-intrinsic Lyn-dependent signaling pathways regulate B cell homeostasis and activation, which in concert with B cell-specific MyD88 signaling pathways can drive the development of autoimmune disease.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Requirement for MyD88 signaling in B cells and dendritic cells for germinal center anti-nuclear antibody production in Lyn-deficient mice.J Immunol. 2014 Feb 1;192(3):875-85. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1300683. Epub 2013 Dec 30. J Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24379120 Free PMC article.
-
IL-21 promotes the production of anti-DNA IgG but is dispensable for kidney damage in lyn-/- mice.Eur J Immunol. 2013 Feb;43(2):382-93. doi: 10.1002/eji.201142095. Epub 2012 Dec 18. Eur J Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23169140 Free PMC article.
-
Hyperactivated MyD88 signaling in dendritic cells, through specific deletion of Lyn kinase, causes severe autoimmunity and inflammation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Aug 27;110(35):E3311-20. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1300617110. Epub 2013 Aug 12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 23940344 Free PMC article.
-
Signaling mutations and autoimmunity.Curr Dir Autoimmun. 2003;6:61-88. doi: 10.1159/000066856. Curr Dir Autoimmun. 2003. PMID: 12408047 Review.
-
Lyn, Lupus, and (B) Lymphocytes, a Lesson on the Critical Balance of Kinase Signaling in Immunity.Front Immunol. 2018 Mar 1;9:401. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00401. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29545808 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Aberrant B Cell Signaling in Autoimmune Diseases.Cells. 2022 Oct 27;11(21):3391. doi: 10.3390/cells11213391. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36359789 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of inhibitory signaling in peripheral B cell tolerance.Immunol Rev. 2022 May;307(1):27-42. doi: 10.1111/imr.13070. Epub 2022 Feb 6. Immunol Rev. 2022. PMID: 35128676 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Loss of CD11b Accelerates Lupus Nephritis in Lyn-Deficient Mice Without Disrupting Glomerular Leukocyte Trafficking.Front Immunol. 2022 May 12;13:875359. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.875359. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35634296 Free PMC article.
-
B cell-intrinsic TLR7 signaling is essential for the development of spontaneous germinal centers.J Immunol. 2014 Nov 1;193(9):4400-14. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1401720. Epub 2014 Sep 24. J Immunol. 2014. PMID: 25252960 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding heterogeneity of human bone marrow plasma cell maturation and survival pathways by single-cell analyses.Cell Rep. 2023 Jul 25;42(7):112682. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2023.112682. Epub 2023 Jun 24. Cell Rep. 2023. PMID: 37355988 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Saijo K, Schmedt C, Su IH, Karasuyama H, Lowell CA, Reth M, Adachi T, Patke A, Santana A, Tarakhovsky A. Essential role of Src-family protein tyrosine kinases in NF-kappaB activation during B cell development. Nature immunology. 2003;4:274–279. - PubMed
-
- Ohashi PS, DeFranco AL. Making and breaking tolerance. Curr Opin Immunol. 2002;14:744–759. - PubMed
-
- DeFranco AL, Chan VW, Lowell CA. Positive and negative roles of the tyrosine kinase Lyn in B cell function. Semin Immunol. 1998;10:299–307. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

