TNM-like classification: a new proposed method for heart failure staging
- PMID: 24376377
- PMCID: PMC3859030
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/175925
TNM-like classification: a new proposed method for heart failure staging
Abstract
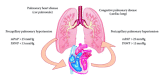
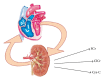
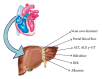
Heart Failure (HF) is an acute or chronic syndrome, that causes a lot of damaging effects to every system. The involvement of different systems is variably related to age and others comorbidities. The severity of organ damage is often proportional to the duration of heart failure. The typology of HF and the duration determine which organs will be affected and vice versa the severity of organ damage supplies precious information about prognosis and outcome of patients with heart failure. Moreover, a classification based not only on symptomatic and syndromic typical features of heart failure, but also on functional data of each system, could allow us to apply the most appropriate therapies, to obtain a more accurate prognosis, and to employ necessary and not redundant human and financial resources. With an eye on the TNM staging used in oncology, we drawn up a classification that will consider the different involvement of organs such as lungs, kidneys, and liver in addition to psychological pattern and quality of life in HF patients. For all these reasons, it is our intention to propose a valid and more specific classification available for the clinical staging of HF that takes into account pathophysiological and structural changes that can remark prognosis and management of HF.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Heart failure in patients with kidney disease.Heart. 2017 Dec;103(23):1848-1853. doi: 10.1136/heartjnl-2016-310794. Epub 2017 Jul 17. Heart. 2017. PMID: 28716974 Review.
-
Utility of strain imaging in conjunction with heart failure stage classification for heart failure patient management.J Echocardiogr. 2019 Mar;17(1):17-24. doi: 10.1007/s12574-018-0408-2. Epub 2018 Nov 15. J Echocardiogr. 2019. PMID: 30443873 Review.
-
Prevalence and prognostic significance of heart failure stages: application of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association heart failure staging criteria in the community.Circulation. 2007 Mar 27;115(12):1563-70. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.106.666818. Epub 2007 Mar 12. Circulation. 2007. PMID: 17353436
-
[The new ESC Guidelines for acute and chronic heart failure 2016].Herz. 2016 Dec;41(8):655-663. doi: 10.1007/s00059-016-4496-3. Herz. 2016. PMID: 27858115 Review. German.
-
Practical management of worsening renal function in outpatients with heart failure and reduced ejection fraction: Statement from a panel of multidisciplinary experts and the Heart Failure Working Group of the French Society of Cardiology.Arch Cardiovasc Dis. 2020 Oct;113(10):660-670. doi: 10.1016/j.acvd.2020.03.018. Epub 2020 Jul 11. Arch Cardiovasc Dis. 2020. PMID: 32660835 Review.
Cited by
-
Structural and myocardial dysfunction in heart failure beyond ejection fraction.Heart Fail Rev. 2020 Jan;25(1):9-17. doi: 10.1007/s10741-019-09828-8. Heart Fail Rev. 2020. PMID: 31317296 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Heart failure: role and point of view of cardiac intensivist.Cardiovasc Diagn Ther. 2021 Feb;11(1):301-308. doi: 10.21037/cdt-20-339. Cardiovasc Diagn Ther. 2021. PMID: 33708501 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Heart failure 'the cancer of the heart': the prognostic role of the HLM score.ESC Heart Fail. 2024 Feb;11(1):390-399. doi: 10.1002/ehf2.14594. Epub 2023 Nov 27. ESC Heart Fail. 2024. PMID: 38011913 Free PMC article.
-
Myocardial Ischemia and Diabetes Mellitus: Role of Oxidative Stress in the Connection between Cardiac Metabolism and Coronary Blood Flow.J Diabetes Res. 2019 Apr 4;2019:9489826. doi: 10.1155/2019/9489826. eCollection 2019. J Diabetes Res. 2019. PMID: 31089475 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advanced Heart Failure and End-Stage Heart Failure: Does a Difference Exist.Diagnostics (Basel). 2019 Nov 1;9(4):170. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics9040170. Diagnostics (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31683887 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Neubauer S. The failing heart—an engine out of fuel. New England Journal of Medicine. 2007;356(11):1140–1151. - PubMed
-
- Krum H, Abraham WT. Heart failure. The Lancet. 2009;373(9667):941–955. - PubMed
-
- Gheorghiade M, Pang PS. Acute heart failure syndromes. Journal of the American College of Cardiology. 2009;53(7):557–573. - PubMed
-
- Hunt SA, Abraham WT, Chin MH, et al. 2009 focused update incorporated into the ACC/AHA 2005 guidelines for the diagnosis and management of heart failure in adults. A Report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines Developed in Collaboration With the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation. Journal of the American College of Cardiology. 2009;53(15):e1–e90. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

