Analytical tools for the study of cellular glycosylation in the immune system
- PMID: 24376449
- PMCID: PMC3858669
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2013.00451
Analytical tools for the study of cellular glycosylation in the immune system
Abstract
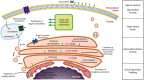
It is becoming increasingly clear that glycosylation plays important role in intercellular communication within the immune system. Glycosylation-dependent interactions are crucial for the innate and adaptive immune system and regulate immune cell trafficking, synapse formation, activation, and survival. These functions take place by the cis or trans interaction of lectins with glycans. Classical immunological and biochemical methods have been used for the study of lectin function; however, the investigation of their counterparts, glycans, requires very specialized methodologies that have been extensively developed in the past decade within the Glycobiology scientific community. This mini-review intends to summarize the available technology for the study of glycan biosynthesis, its regulation and characterization for their application to the study of glycans in immunology.
Keywords: glycan analysis; glycans; glycosyltransferases; immune cells; lectins.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

