Pulmonary delivery of an ultra-fine oxytocin dry powder formulation: potential for treatment of postpartum haemorrhage in developing countries
- PMID: 24376618
- PMCID: PMC3871608
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0082965
Pulmonary delivery of an ultra-fine oxytocin dry powder formulation: potential for treatment of postpartum haemorrhage in developing countries
Abstract
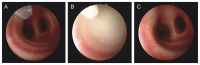
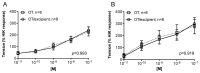
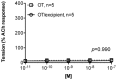
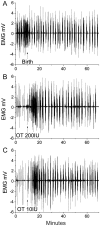
Oxytocin is recommended by the World Health Organisation as the most effective uterotonic for the prevention and treatment of postpartum haemorrhage. The requirement for parenteral administration by trained healthcare providers and the need for the drug solution to be maintained under cold-chain storage limit the use of oxytocin in the developing world. In this study, a spray-dried ultrafine formulation of oxytocin was developed with an optimal particle size diameter (1-5 µm) to facilitate aerosolised delivery via the lungs. A powder formulation of oxytocin, using mannitol, glycine and leucine as carriers, was prepared with a volume-based median particle diameter of 1.9 µm. Oxytocin content in the formulation was assayed using high-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectroscopy and was found to be unchanged after spray-drying. Ex vivo contractility studies utilising human and ovine uterine tissue indicated no difference in the bioactivity of oxytocin before and after spray-drying. Uterine electromyographic (EMG) activity in postpartum ewes following pulmonary (in vivo) administration of oxytocin closely mimicked that observed immediately postpartum (0-12 h following normal vaginal delivery of the lamb). In comparison to the intramuscular injection, pulmonary administration of an oxytocin dry powder formulation to postpartum ewes resulted in generally similar EMG responses, however a more rapid onset of uterine EMG activity was observed following pulmonary administration (129 ± 18 s) than intramuscular injection (275 ± 22 s). This is the first study to demonstrate the potential for oxytocin to elicit uterine activity after systemic absorption as an aerosolised powder from the lungs. Aerosolised oxytocin has the potential to provide a stable and easy to administer delivery system for effective prevention and treatment of postpartum haemorrhage in resource-poor settings in the developing world.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- WHO (2012) WHO Recommendations for the prevention and treatment of postpartum haemorrhage. Geneva: WHO. - PubMed
-
- WHO (2011) FINAL Report of the 18th Expert Committee on the Selection and Use of Essential Medicines (WHO TRS 965).
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

