Beam rate influence on dose distribution and fluence map in IMRT dynamic technique
- PMID: 24377007
- PMCID: PMC3863304
- DOI: 10.1016/j.rpor.2012.01.004
Beam rate influence on dose distribution and fluence map in IMRT dynamic technique
Abstract
Aim: To examine the impact of beam rate on dose distribution in IMRT plans and then to evaluate agreement of calculated and measured dose distributions for various beam rate values.
Background: Accelerators used in radiotherapy utilize some beam rate modes which can shorten irradiation time and thus reduce ability of patient movement during a treatment session. This aspect should be considered in high conformal dynamic techniques.
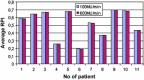
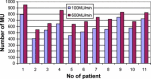
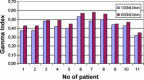
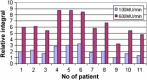
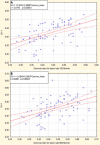
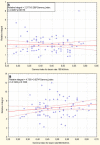
Materials and methods: Dose calculation was done for two different beam rates (100 MU/min and 600 MU/min) in an IMRT plan. For both, a comparison of Radiation Planning Index (RPI) and MU was conducted. Secondly, the comparison of optimal fluence maps and corresponding actual fluence maps was done. Next, actual fluence maps were measured and compared with the calculated ones. Gamma index was used for that assessment. Additionally, positions of each leaf of the MLC were controlled by home made software.
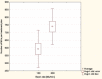
Results: Dose distribution obtained for lower beam rates was slightly better than for higher beam rates in terms of target coverage and risk structure protection. Lower numbers of MUs were achieved in 100 MU/min plans than in 600 MU/min plans. Actual fluence maps converted from optimal ones demonstrated more similarity in 100 MU/min plans. Better conformity of the measured maps to the calculated ones was obtained when a lower beam rate was applied. However, these differences were small. No correlation was found between quality of fluence map conversion and leaf motion accuracy.
Conclusion: Execution of dynamic techniques is dependent on beam rate. However, these differences are minor. Analysis shows a slight superiority of a lower beam rate. It does not significantly affect treatment accuracy.
Keywords: Dose rate; Fluence map; Gamma index; IMRT.
Figures


References
-
- Dong L., Mohan R. Intensity-modulated radiation therapy physics and quality assurance. In: Chao K.S.C., Apisarnthanarax S., Ozyigit G., editors. Practical essentials of intensity modulated radiation therapy. 2nd ed. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; Philadelphia: 2005. pp. 1–19.
-
- Intensity Modulated Radiation Therapy Collaborative Working Group Intensity-modulated radiotherapy: current status and issues of interestInt J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2001;51:880–914. - PubMed
-
- Xia P. Optimization of intensity-modulated radiation therapy treatment planning. In: Chao K.S.C., Apisarnthanarax S., Ozyigit G., editors. Practical essentials of intensity modulated radiation therapy. 2nd ed. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; Philadelphia: 2005. pp. 20–29.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

